Summary: Domestic cats choose not a contrafreeload, a behavior where most animals prefer to work for their food.
Source: UC Davis
When given the choice between a free meal and performing a task for a meal, cats would prefer the meal that doesn’t require much effort. While that might not come as a surprise to some cat lovers, it does to cat behaviorists. Most animals prefer to work for their food — a behavior called contrafreeloading.
A new study from researchers at the University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine showed most domestic cats choose not to contrafreeload. The study found that cats would rather eat from a tray of easily available food rather than work out a simple puzzle to get their food.
“There is an entire body of research that shows that most species including birds, rodents, wolves, primates — even giraffes — prefer to work for their food,” said lead author Mikel Delgado, a cat behaviorist and research affiliate at UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine.

“What’s surprising is out of all these species cats seem to be the only ones that showed no strong tendency to contrafreeload.”
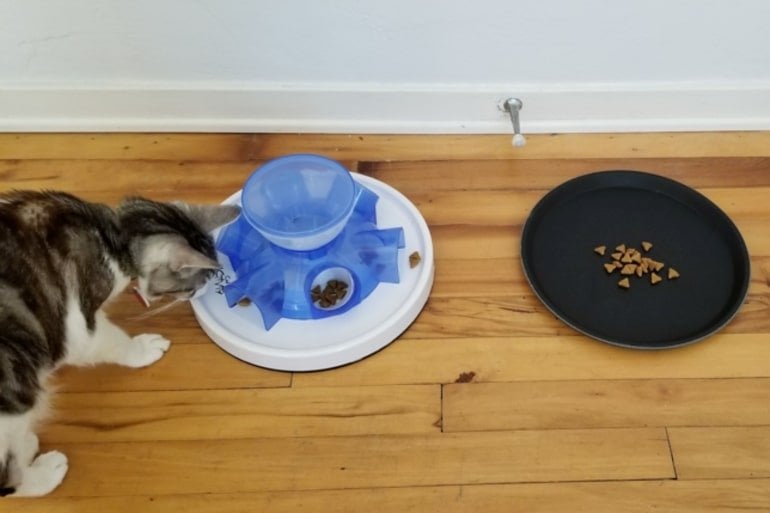
In the study, Delgado, along with co-authors Melissa Bain and Brandon Han of the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine, provided 17 cats a food puzzle and a tray of food. The puzzle allowed the cats to easily see the food but required some manipulation to extract it. Some of the cats even had food puzzle experience.
“It wasn’t that cats never used the food puzzle, but cats ate more food from the tray, spent more time at the tray and made more first choices to approach and eat from the tray rather than the puzzle,” said Delgado.
Cats aren’t just lazy
Cats that were part of the study wore activity monitors. The study found that even cats that were more active still chose the freely available food. Delgado said the study should not be taken as a dismissal of food puzzles. She said just because they don’t prefer it, doesn’t mean they don’t like it. Delgado’s previous research shows puzzles can be an important enrichment activity for cats.
Why cats prefer to freeload is also unclear. Delgado said the food puzzles used in the study may not have stimulated their natural hunting behavior, which usually involves ambushing their prey.
Funding: The study was published in the journal Animal Cognition. The research was supported by Maddie’s Fund and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
About this animal psychology research news
Author: Amy Quinton
Source: UC Davis
Contact: Amy Quinton – UC Davis
Image: The image is credited to Mikel Delgado/UC Davis
Original Research: Open access.
“Domestic cats (Felis catus) prefer freely available food over food that requires effort” by Mikel Delgado et al. Animal Cognition
Abstract
Domestic cats (Felis catus) prefer freely available food over food that requires effort
Contrafreeloading is the willingness of animals to work for food when equivalent food is freely available. This behavior is observed in laboratory, domesticated, and captive animals. However, previous research found that six laboratory cats failed to contrafreeload.
We hypothesized that cats would contrafreeload in the home environment when given a choice between a food puzzle and a tray of similar size and shape. We also hypothesized that more active cats would be more likely to contrafreeload.
We assessed the behavior of 17 neutered, indoor domestic cats (Felis catus) when presented with both a food puzzle and a tray across ten 30-min trials. Each cat wore an activity tracker, and all sessions were video recorded.
Cats ate more food from the free feed tray than the puzzle (t (16) = 6.77, p < 0.001). Cats made more first choices to approach and eat from the tray. There was no relationship between activity and contrafreeloading, and there was no effect of sex, age, or previous food puzzle experience on contrafreeloading.
Our results suggest that cats do not show strong tendencies to contrafreeload in the home environment, although some cats (N = 4) ate most food offered in the puzzle or showed weak contrafreeloading tendencies (N = 5). Eight cats did not contrafreeload. Cats who consumed more food from the puzzle, consumed more food in general, suggesting a relationship between hunger and effort.
Further research is required to understand why domestic cats, unlike other tested species, do not show a strong preference to work for food.