Summary: Researchers report the cytomegalovirus may actually boost, not weaken, our immune systems.
Source: University of Arizona.
Our immune system is at its peak when we’re young, but after a certain age, it declines and it becomes more difficult for our bodies to fight off new infections.
“That’s why older people are more susceptible to infections than younger people,” explains Janko Nikolich-Zugich, MD, PhD, co-director or the University of Arizona Center on Aging and chairman of the Department of Immunobiology at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson.
In search of a way to rejuvenate the immune system of older adults, Dr. Nikolich-Zugich and Megan Smithey, PhD, have found that one particular virus may not weaken, but actually enhance our immune system. Their findings are published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
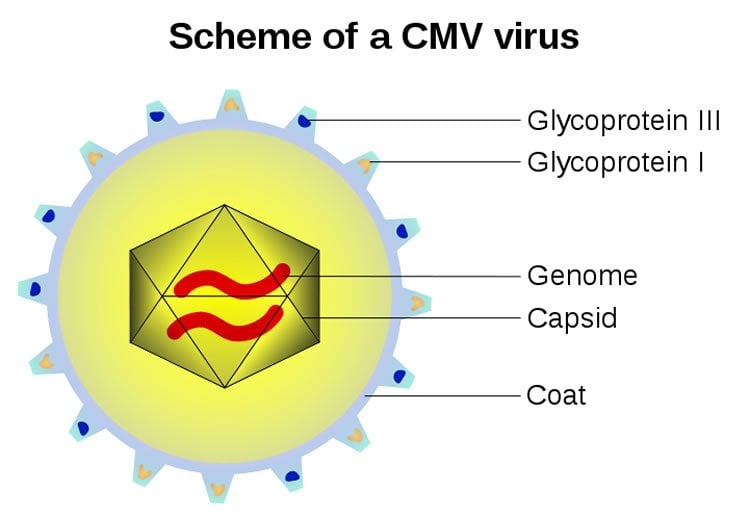
For the study, the researchers infected mice with the cytomegalovirus (CMV). The virus affects more than half of all individuals and is contracted, for most part, at a young age. Because there is no cure, the virus is carried for life, and is particularly prevalent in older adults.
“CMV doesn’t usually cause outward symptoms, but we still have to live with it every day since there’s no cure,” Dr. Smithey says. “Our immune system always will be busy in the background dealing with this virus.”
Drs. Smithey and Nikolich-Zugich wondered how this lifelong virus ultimately affects the immune system.
“We assumed it would make mice more vulnerable to other infections because it was using up resources and keeping the immune system busy,” Dr. Smithey said.
But that’s not what happens.
When infected with listeria, old mice carrying CMV proved to be tougher than old mice without CMV.
“We were completely surprised; we expected these mice to be worse off,” Smithey says. “But they had a more robust, effective response to the infection.”
The researchers are not certain how CMV strengthens the immune system — they are investigating that in a separate study — but they do believe they have gained new insight into the aging immune system.
“This study shows us that there is more capacity in the immune system at an older age than we thought,” Dr. Smithey says.
When the researchers examined the mice’s T-cells — the army of defenders that fights off infection — they found that both groups of older mice had a decent supply of diverse T-cells.
“Diversity is good,” Dr. Nikolich-Zugich says. “Different types of T-cells respond to different types of infections; the more diverse T-cells you have, the more likely you’ll be able to fight off infections.”
For years, immunobiologists assumed that T-cell diversity decreased as we age. This was one of the reasons why older adults succumbed to disease more easily.
But Drs. Smithey and Nikolich-Zugich’s new study shows that T-cells are almost as diverse in old mice as they are in young mice. The problem is that diverse T-cells are not recruited to the battlefield in older mice — unless they are infected with CMV.
Dr. Nikolich-Zugich explains, “It’s as if CMV is issuing a signal that gets the best defenses out onto the field.”
“This shows that the ability to generate a good immune response exists in old age — and CMV, or the body’s response to CMV, can help harness that ability,” Dr. Smithey adds.
The UA College of Medicine – Tucson team plans to continue to study CMV. It hopes to see similar results in human studies. The team’s ultimate goal is to create a vaccine that can improve the immune system of older adults and protect against infection.
Funding: The studies were supported by a grant from the National Institute on Aging, one of the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. Nikolich Zugich also is a member of the UA BIO5 Institute. Dr. Smithey is a research assistant professor who specializes in immunobiology and a member of the Arizona Center on Aging.
Source: Nadia Whitehead – University of Arizona
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Emmanuel Boutet. Licensed CC BY SA 2.5.
Original Research: Abstract for “Lifelong CMV infection improves immune defense in old mice by broadening the mobilized TCR repertoire against third-party infection” by Megan J. Smithey, Vanessa Venturi, Miles P. Davenport, Adam S. Buntzman, Benjamin G. Vincent, Jeffrey A. Frelinger, and Janko Nikolich-Žugich in PNAS. Published July 2 2028.
doi:10.1073/pnas.1719451115
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]University of Arizona”CMV Virus May Boost Our Immune System.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 2 July 2028.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/cmv-virus-immune-system-9498/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]University of Arizona(2028, July 2). CMV Virus May Boost Our Immune System. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved July 2, 2028 from https://neurosciencenews.com/cmv-virus-immune-system-9498/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]University of Arizona”CMV Virus May Boost Our Immune System.” https://neurosciencenews.com/cmv-virus-immune-system-9498/ (accessed July 2, 2028).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Lifelong CMV infection improves immune defense in old mice by broadening the mobilized TCR repertoire against third-party infection
Lifelong interactions between host and the ubiquitous and persistent cytomegalovirus (CMV) have been proposed to contribute to the age-related decline in immunity. Prior work from us and others found some support for that idea, yet evidence that this led to increased vulnerability to other infections was not obtained. Moreover, evidence has accumulated that CMV infection can be beneficial to immune defense in young/adult mice and humans, dominantly via enhanced innate immunity. Here, we describe an unexpected impact of murine CMV (MCMV) upon the T cell response of old mice to Listeria monocytogenes expressing the model antigen, OVA (Lm-OVA). Single-cell sequencing of the OVA-specific CD8 T cell receptor β (TCRβ) repertoire of old mice demonstrated that old MCMV-infected mice recruited many diverse clonotypes that afforded broad and often more efficient recognition of antigenic peptide variants. This stood in contrast to old control mice, which exhibited strong narrowing and homogenization of the elicited repertoire. High-throughput sequencing of the total naïve CD8 TCRβ repertoire showed that many of these diverse OVA-specific clonotypes were present in the naïve CD8 repertoire of mice in all groups (adult, old control, and old MCMV+) yet were only recruited into the Lm-OVA response in MCMV+ old mice. These results have profound implications for our understanding of T cell immunity over a life span and suggest that our coevolution with CMV may include surprising, potentially positive impacts on adaptive heterologous immunity in late life.