An SDSU research team has discovered that autism in children affects not only social abilities, but also a broad range of sensory and motor skills.
A group of investigators from San Diego State University’s Brain Development Imaging Laboratory are shedding a new light on the effects of autism on the brain.
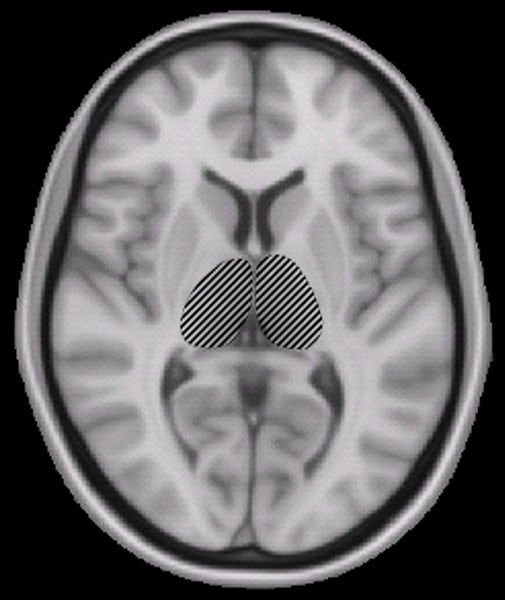
The team has identified that connectivity between the thalamus, a deep brain structure crucial for sensory and motor functions, and the cerebral cortex, the brain’s outer layer, is impaired in children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD).
Led by Aarti Nair, a student in the SDSU/UCSD Joint Doctoral Program in Clinical Psychology, the study is the first of its kind, combining functional and anatomical magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) techniques and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to examine connections between the cerebral cortex and the thalamus.

Nair and Dr. Ralph-Axel Müller, an SDSU professor of psychology who was senior investigator of the study, examined more than 50 children, both with autism and without.
Brain communication
The thalamus is a crucial brain structure for many functions, such as vision, hearing, movement control and attention. In the children with autism, the pathways connecting the cerebral cortex and thalamus were found to be affected, indicating that these two parts of the brain do not communicate well with each other.
“This impaired connectivity suggests that autism is not simply a disorder of social and communicative abilities, but also affects a broad range of sensory and motor systems,” Müller said.
Disturbances in the development of both the structure and function of the thalamus may play a role in the emergence of social and communicative impairments, which are among the most prominent and distressing symptoms of autism.
While the findings reported in this study are novel, they are consistent with growing evidence on sensory and motor abnormalities in autism. They suggest that the diagnostic criteria for autism, which emphasize social and communicative impairment, may fail to consider the broad spectrum of problems children with autism experience.
Notes about this autism research
The study was supported with funding from the National Institutes of Health and additional funding from Autism Speaks Dennis Weatherstone Predoctoral Fellowship. It was published in the June issue of the journal, BRAIN.
Written by Natalia Van Stralen
Contact: Natalia Van Stralen – SDSU
Source: SDSU press release
Image Source: The MRI brain scan is credited to Woutergroen and is in the public domain.
Original Research: Abstract for “Impaired thalamocortical connectivity in autism spectrum disorder: a study of functional and anatomical connectivity” by Aarti Nair, Jeffrey M. Treiber, Dinesh K. Shukla, Patricia Shih and Ralph-Axel Müller in BRAIN. Published online June 2013 doi: 10.1093/brain/awt079