Summary: Researchers have identified how specific genetic mutations cause ALS. The pathway, they believe, may also be responsible for the development of frontotemporal dementia.
Source: University of Maryland School of Medicine
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have identified how certain gene mutations cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease. The pathway identified by the researchers may also be responsible for a certain form of dementia related to ALS. The finding could offer potential new approaches for treating this devastating condition, which causes progressive, fatal paralysis and sometimes mental deterioration similar to Alzheimer’s disease. Their discovery was published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) and included collaborators from Harvard University, University of Auckland, King’s College London, and Northwestern University.
More than 5,000 Americans are diagnosed with ALS every year, a condition that is usually fatal and has no cure. Patients with ALS slowly lose the ability to move their muscles, leading to problems with basic functions such as breathing and swallowing. About half of ALS patients also develop dementia. Genetic studies of families with a predisposition to develop ALS have shown that the condition can be associated with certain gene mutations. Some of these mutations involve the gene UBQLN2 which regulates the disposal of misfolded “garbage” from the body’s cells. Until now, researchers did not fully understand how UBQLN2 mutations interfere with this pathway and cause ALS.
“We mapped out the process by which ubiquilin-2 (UBQLN2) gene mutations disrupt an important recycling pathway that cells use to get rid of their trash,” said Mervyn Monteiro, PhD, Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology, who is affiliated with the UMSOM’s Center for Biomedical Engineering and Technology (BioMET) at UMSOM. “Without this recycling, misfolded proteins build up in the nerve cell and become toxic, eventually destroying the cell. This destruction could lead to neurodegenerative disorders like ALS.”
To investigate how UBQLN2 mutations cause ALS, Dr. Monteiro’s group used both human cells and UBQLN2-mutant mouse models for their investigations. The mouse models, which they described in a 2016 PNAS publication, mimic the progression of the disease in people who inherit these gene mutations.
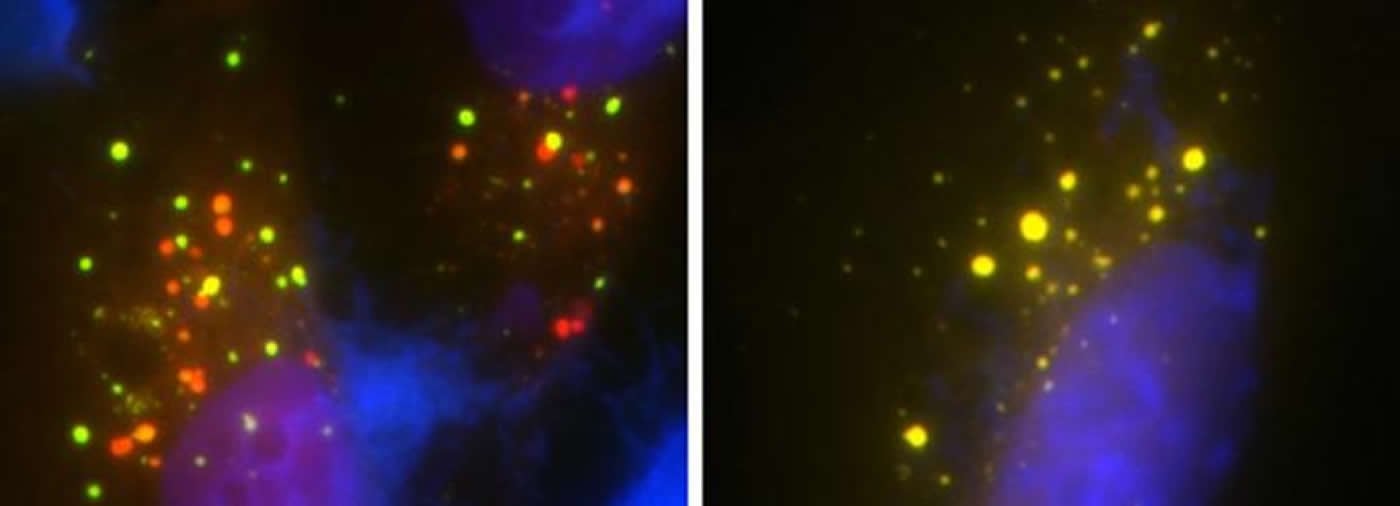
Dr. Monteiro’s group first removed the UBQLN2 gene from human cells and found it completely stalled the recycling pathway. They then reintroduced either the normal gene or one of five gene mutations into the cells. They found that reintroduction of normal UBQLN2 restored the recycling pathway while all five of the gene mutations failed to restart the pathway.
Using the mouse model, Dr. Monteiro and his colleagues outlined the reason for the pathway disruption in the presence of gene mutations. They found that the mice with the gene mutations had reduced levels of a certain protein called ATP6v1g1, which is an essential part of a pump that acidifies the cell’s trash container in order to initiate the breakdown and recycling process.
“Our new findings are exciting because similar acidification defects have been found in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Down syndrome,” Dr. Monteiro said. “This suggests that restoration of the defect could have broad implications for not only treating ALS, but possibly other neurodegenerative diseases as well.”
The research study was supported by grants from the Packard Center for ALS Research at Johns Hopkins, the ALS Association, and the National Institutes of Health (grant number: R01-NS100008).
“The BioMET research team led by Dr. Monteiro continues to make important advances in understanding the mechanisms that give rise to ALS,” said Dean E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, who is also Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, UM Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “Future treatments and preventive measures for this devastating disease would not be possible without this foundational work.”
About this neuroscience research article
Source:
University of Maryland School of Medicine
Media Contacts:
Deborah Kotz – University of Maryland School of Medicine
Image Source:
The image is credited to University of Maryland School of Medicine.
Original Research: Closed access
“ALS/FTD mutations in UBQLN2 impede autophagy by reducing autophagosome acidification through loss of function”. by Mervyn Monteiro et al.
PNAS doi:10.1073/pnas.1917371117
Abstract
ALS/FTD mutations in UBQLN2 impede autophagy by reducing autophagosome acidification through loss of function
Mutations in UBQLN2 cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and other neurodegenerations. However, the mechanism by which the UBQLN2 mutations cause disease remains unclear. Alterations in proteins involved in autophagy are prominent in neuronal tissue of human ALS UBQLN2 patients and in a transgenic P497S UBQLN2 mouse model of ALS/FTD, suggesting a pathogenic link. Here, we show UBQLN2 functions in autophagy and that ALS/FTD mutant proteins compromise this function. Inactivation of UBQLN2 expression in HeLa cells reduced autophagic flux and autophagosome acidification. The defect in acidification was rescued by reexpression of wild type (WT) UBQLN2 but not by any of the five different UBQLN2 ALS/FTD mutants tested. Proteomic analysis and immunoblot studies revealed P497S mutant mice and UBQLN2 knockout HeLa and NSC34 cells have reduced expression of ATP6v1g1, a critical subunit of the vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase) pump. Knockout of UBQLN2 expression in HeLa cells decreased turnover of ATP6v1g1, while overexpression of WT UBQLN2 increased biogenesis of ATP6v1g1 compared with P497S mutant UBQLN2 protein. In vitro interaction studies showed that ATP6v1g1 binds more strongly to WT UBQLN2 than to ALS/FTD mutant UBQLN2 proteins. Intriguingly, overexpression of ATP6v1g1 in UBQLN2 knockout HeLa cells increased autophagosome acidification, suggesting a therapeutic approach to overcome the acidification defect. Taken together, our findings suggest that UBQLN2 mutations drive pathogenesis through a dominant-negative loss-of-function mechanism in autophagy and that UBQLN2 functions as an important regulator of the expression and stability of ATP6v1g1. These findings may have important implications for devising therapies to treat UBQLN2-linked ALS/FTD.
Feel Free To Share This Neuroscience News.