Summary: The ARHGAP11B gene played a critical role in the development of the human neocortex during evolution.
Source: DPZ
Animal studies on great apes have long been banned in Europe for ethical reasons. For the question pursued here, so-called organoids, i.e. three-dimensional cell structures a few millimeters in size that are grown in the laboratory, are an alternative to animal experiments.
These organoids can be produced from pluripotent stem cells, which then differentiate into specific cell types, such as nerve cells. In this way, the research team was able to produce both chimpanzee brain organoids and human brain organoids.
“These brain organoids allowed us to investigate a central question concerning ARHGAP11B,” says Wieland Huttner of the MPI-CBG, one of the three lead authors of the study.
“In a previous study we were able to show that ARHGAP11B can enlarge a primate brain. However, it was previously unclear whether ARHGAP11B had a major or minor role in the evolutionary enlargement of the human neocortex,” says Wieland Huttner.
To clarify this, the ARGHAP11B gene was first inserted into brain ventricle-like structures of chimpanzee organoids. Would the ARGHAP11B gene lead to the proliferation of those brain stem cells in the chimpanzee brain that are necessary for the enlargement of the neocortex?
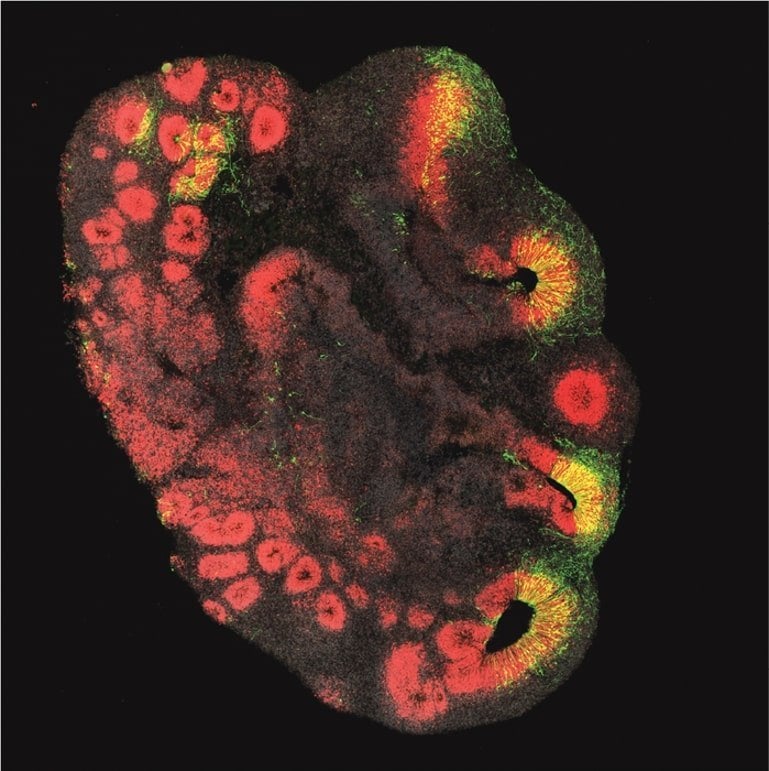
“Our study shows that the gene in chimpanzee organoids causes an increase in relevant brain stem cells and an increase in those neurons that play a crucial role in the extraordinary mental abilities of humans,” said Michael Heide, the study’s lead author, who is head of the Junior Research Group Brain Development and Evolution at the DPZ and employee at the MPI-CBG.
When the ARGHAP11B gene was knocked out in human brain organoids or the function of the ARHGAP11B protein was inhibited, the amount of these brain stem cells decreased to the level of a chimpanzee.
“We were thus able to show that ARHGAP11B plays a crucial role in neocortex development during human evolution,” says Michael Heide. Julia Ladewig of HITBR, the third of the lead authors, adds:
“Given this important role of ARHGAP11B, it is furthermore conceivable that certain maldevelopments of the neocortex may be caused by mutations in this gene.”
About this genetics and evolutionary neuroscience research news
Author: Susanne Diederich
Source: DPZ
Contact: Susanne Diederich – DPZ
Image: The image is credited to Jan Fischer
Original Research: Open access.
“Human-specific ARHGAP11B ensures human-like basal progenitor levels in hominid cerebral organoids” by Michael Heide et al. EMBO Reports
Abstract
Human-specific ARHGAP11B ensures human-like basal progenitor levels in hominid cerebral organoids
The human-specific gene ARHGAP11B has been implicated in human neocortex expansion. However, the extent of ARHGAP11B‘s contribution to this expansion during hominid evolution is unknown.
Here we address this issue by genetic manipulation of ARHGAP11B levels and function in chimpanzee and human cerebral organoids. ARHGAP11B expression in chimpanzee cerebral organoids doubles basal progenitor levels, the class of cortical progenitors with a key role in neocortex expansion. Conversely, interference with ARHGAP11B’s function in human cerebral organoids decreases basal progenitors down to the chimpanzee level.
Moreover, ARHGAP11A or ARHGAP11B rescue experiments in ARHGAP11A plus ARHGAP11B double-knockout human forebrain organoids indicate that lack of ARHGAP11B, but not of ARHGAP11A, decreases the abundance of basal radial glia—the basal progenitor type thought to be of particular relevance for neocortex expansion.
Taken together, our findings demonstrate that ARHGAP11B is necessary and sufficient to ensure the elevated basal progenitor levels that characterize the fetal human neocortex, suggesting that this human-specific gene was a major contributor to neocortex expansion during human evolution.






