Summary: Researchers at MIT have developed a new neuroimaging technique that can track signaling processes inside neurons. The MRI sensor will enable researchers to identify the roles neurons play in different types of behavior.
Source: MIT.
Calcium is a critical signaling molecule for most cells, and it is especially important in neurons. Imaging calcium in brain cells can reveal how neurons communicate with each other; however, current imaging techniques can only penetrate a few millimeters into the brain.
MIT researchers have now devised a new way to image calcium activity that is based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and allows them to peer much deeper into the brain. Using this technique, they can track signaling processes inside the neurons of living animals, enabling them to link neural activity with specific behaviors.
“This paper describes the first MRI-based detection of intracellular calcium signaling, which is directly analogous to powerful optical approaches used widely in neuroscience but now enables such measurements to be performed in vivo in deep tissue,” says Alan Jasanoff, an MIT professor of biological engineering, brain and cognitive sciences, and nuclear science and engineering, and an associate member of MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research.
Jasanoff is the senior author of the paper, which appears in the Feb. 22 issue of Nature Communications. MIT postdocs Ali Barandov and Benjamin Bartelle are the paper’s lead authors. MIT senior Catherine Williamson, recent MIT graduate Emily Loucks, and Arthur Amos Noyes Professor Emeritus of Chemistry Stephen Lippard are also authors of the study.
Getting into cells
In their resting state, neurons have very low calcium levels. However, when they fire an electrical impulse, calcium floods into the cell. Over the past several decades, scientists have devised ways to image this activity by labeling calcium with fluorescent molecules. This can be done in cells grown in a lab dish, or in the brains of living animals, but this kind of microscopy imaging can only penetrate a few tenths of a millimeter into the tissue, limiting most studies to the surface of the brain.
“There are amazing things being done with these tools, but we wanted something that would allow ourselves and others to look deeper at cellular-level signaling,” Jasanoff says.
To achieve that, the MIT team turned to MRI, a noninvasive technique that works by detecting magnetic interactions between an injected contrast agent and water molecules inside cells.
Many scientists have been working on MRI-based calcium sensors, but the major obstacle has been developing a contrast agent that can get inside brain cells. Last year, Jasanoff’s lab developed an MRI sensor that can measure extracellular calcium concentrations, but these were based on nanoparticles that are too large to enter cells.
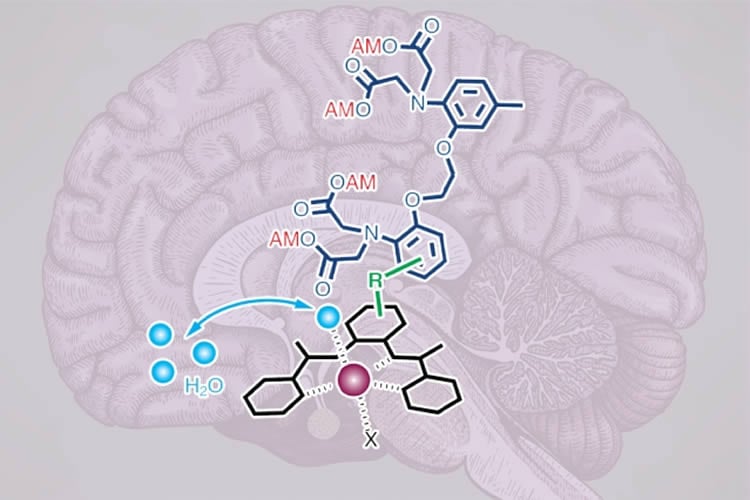
To create their new intracellular calcium sensors, the researchers used building blocks that can pass through the cell membrane. The contrast agent contains manganese, a metal that interacts weakly with magnetic fields, bound to an organic compound that can penetrate cell membranes. This complex also contains a calcium-binding arm called a chelator.
Once inside the cell, if calcium levels are low, the calcium chelator binds weakly to the manganese atom, shielding the manganese from MRI detection. When calcium flows into the cell, the chelator binds to the calcium and releases the manganese, which makes the contrast agent appear brighter in an MRI image.
“When neurons, or other brain cells called glia, become stimulated, they often experience more than tenfold increases in calcium concentration. Our sensor can detect those changes,” Jasanoff says.
Precise measurements
The researchers tested their sensor in rats by injecting it into the striatum, a region deep within the brain that is involved in planning movement and learning new behaviors. They then used potassium ions to stimulate electrical activity in neurons of the striatum, and were able to measure the calcium response in those cells.
Jasanoff hopes to use this technique to identify small clusters of neurons that are involved in specific behaviors or actions. Because this method directly measures signaling within cells, it can offer much more precise information about the location and timing of neuron activity than traditional functional MRI (fMRI), which measures blood flow in the brain.
“This could be useful for figuring out how different structures in the brain work together to process stimuli or coordinate behavior,” he says.
In addition, this technique could be used to image calcium as it performs many other roles, such as facilitating the activation of immune cells. With further modification, it could also one day be used to perform diagnostic imaging of the brain or other organs whose functions rely on calcium, such as the heart.
Funding: The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the MIT Simons Center for the Social Brain.
Source: Anne Trafton – MIT
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to the researchers.
Original Research: Open access research for “Sensing intracellular calcium ions using a manganese-based MRI contrast agent” by Ali Barandov, Benjamin B. Bartelle, Catherine G. Williamson, Emily S. Loucks, Stephen J. Lippard & Alan Jasanoff in Nature Communications. Published February 22 2019.
doi:10.1038/s41598-019-39696-z
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]MIT”New MRI Sensor Can Image Activity Deep Within the Brain.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 22 February 2019.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/mri-sensor-brain-imaging-10795/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]MIT(2019, February 22). New MRI Sensor Can Image Activity Deep Within the Brain. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved February 22, 2019 from https://neurosciencenews.com/mri-sensor-brain-imaging-10795/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]MIT”New MRI Sensor Can Image Activity Deep Within the Brain.” https://neurosciencenews.com/mri-sensor-brain-imaging-10795/ (accessed February 22, 2019).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Sensing intracellular calcium ions using a manganese-based MRI contrast agent
Calcium ions are essential to signal transduction in virtually all cells, where they coordinate processes ranging from embryogenesis to neural function. Although optical probes for intracellular calcium imaging have been available for decades, the development of probes for noninvasive detection of intracellular calcium signaling in deep tissue and intact organisms remains a challenge. To address this problem, we synthesized a manganese-based paramagnetic contrast agent, ManICS1-AM, designed to permeate cells, undergo esterase cleavage, and allow intracellular calcium levels to be monitored by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Cells loaded with ManICS1-AM show changes in MRI contrast when stimulated with pharmacological agents or optogenetic tools; responses directly parallel the signals obtained using fluorescent calcium indicators. Introduction of ManICS1-AM into rodent brains furthermore permits MRI-based measurement of neural activation in optically inaccessible brain regions. These results thus validate ManICS1-AM as a calcium sensor compatible with the extensive penetration depth and field of view afforded by MRI.






