Summary: A new study reveals a mechanism that may explain how the brain is able to retain memories when faced with distraction. The findings could help with the development of new artificial neural networks and AI technology.
Source: National University of Singapore.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have recently discovered a mechanism that could explain how the brain retains working memory when faced with distractions. These findings could endow cognitive flexibility to neural networks used for artificial intelligence.
Working memory is a form of short-term memory responsible for storing and managing the information required to carry out everyday cognitive tasks such as reasoning and language comprehension. It operates over short time scales and allows us to focus our attention, resist distractions and guide our decision-making. For instance, when we remember a telephone number that we want to dial or perform a mental calculation, we are using our working memory. Importantly, we are able to carry on with these tasks even in the presence of temporary distractions, for instance, when the task is being interrupted or when we receive new information.
The prefrontal cortex plays a central role in the maintenance of working memory and the suppression of distractors. Past studies have shown that working memory is stored in the activity of populations of neurons in the prefrontal cortex through unchanging neural activity, suggesting that activity of the neurons is unaffected by distractions, allowing for information to be retained.
However, studies conducted by the NUS team suggest that distractions do change the activity of the neurons, but they are able to retain information by reorganising the information within the same population of neurons. In other words, the “code” used by the neurons to maintain memory information morphs to a different code after a distractor is presented. This unexpected finding has strong implications for our understanding of how the brain processes information, which in turn may lead to inspiration for research in artificial intelligence, as well as neuropsychiatric research, where deficits in memory and attention are common.
The research team behind this novel discovery was led by Assistant Professor Yen Shih-Cheng from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at NUS Faculty of Engineering and Assistant Professor Camilo Libedinsky from the Department of Psychology at NUS Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences.
The team’s findings were published online in the prestigious scientific journal Nature Neuroscience on 9 October 2017.
Inspiration for novel and more efficient neural networks
The brain uses incredibly sophisticated mechanisms to store information very efficiently and reliably. The findings of this study provide new insights into how the brain works, and suggest a mechanism for small populations of neurons to flexibly store different types of information.
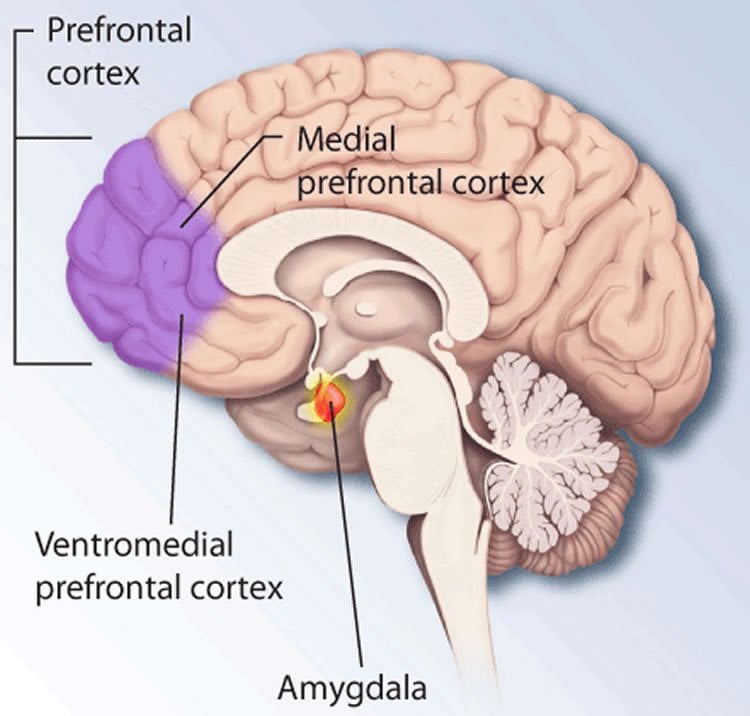
“Our study could potentially provide inspiration for new types of computer architectures and learning rules used in artificial neural networks modelled after the brain. This could potentially enhance the neural network’s ability to store information flexibly using fewer resources, and to exhibit greater resilience in retaining information in these networks – for instance, in the presence of new incoming information or disruption to the activity,” said Asst Prof Yen.
“Another interesting aspect of this study is to consider the results within the context of abnormal brain function. We found that when memory is disturbed, the code fails to reorganise the neurons appropriately. Patients with Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia and dementia show declines in working memory. We would like to explore whether the mechanisms we uncovered could help explain these memory deficits,” said Asst Prof Libedinsky.
Moving forward, the team plans to conduct further studies to understand the conditions that trigger the reorganisation of information in the populations of neurons in the prefrontal cortex. The team is also interested to study how the information is reorganised, and whether this affects activity in other parts of the brain. Furthermore, the researchers hope to use the findings of the study to develop novel neural network architectures.
Source: Amal Naquiah – National University of Singapore
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is in the public domain.
Original Research: Abstract for “Mixed selectivity morphs population codes in prefrontal cortex” by Aishwarya Parthasarathy, Roger Herikstad, Jit Hon Bong, Felipe Salvador Medina, Camilo Libedinsky & Shih-Cheng Yen in Nature Neuroscience. Published online October 18 2017 doi:10.1038/s41593-017-0003-2
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]National University of Singapore “How the Brain Beats Distraction to Retain Memories.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 1 November 2017.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/memory-distraction-7851/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]National University of Singapore (2017, November 1). How the Brain Beats Distraction to Retain Memories. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved November 1, 2017 from https://neurosciencenews.com/memory-distraction-7851/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]National University of Singapore “How the Brain Beats Distraction to Retain Memories.” https://neurosciencenews.com/memory-distraction-7851/ (accessed November 1, 2017).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Mixed selectivity morphs population codes in prefrontal cortex
The prefrontal cortex maintains working memory information in the presence of distracting stimuli. It has long been thought that sustained activity in individual neurons or groups of neurons was responsible for maintaining information in the form of a persistent, stable code. Here we show that, upon the presentation of a distractor, information in the lateral prefrontal cortex was reorganized into a different pattern of activity to create a morphed stable code without losing information. In contrast, the code in the frontal eye fields persisted across different delay periods but exhibited substantial instability and information loss after the presentation of a distractor. We found that neurons with mixed-selective responses were necessary and sufficient for the morphing of code and that these neurons were more abundant in the lateral prefrontal cortex than the frontal eye fields. This suggests that mixed selectivity provides populations with code-morphing capability, a property that may underlie cognitive flexibility.
“Mixed selectivity morphs population codes in prefrontal cortex” by Aishwarya Parthasarathy, Roger Herikstad, Jit Hon Bong, Felipe Salvador Medina, Camilo Libedinsky & Shih-Cheng Yen in Nature Neuroscience. Published online October 18 2017 doi:10.1038/s41593-017-0003-2