Summary: Deep brain stimulation may elevate, and even eliminate symptoms of depression in patients for whom traditional treatments have failed, a new study reports.
Source: University of Freiburg.
Treatment with deep brain stimulation can provide lasting relief to patients suffering from previously non-treatable, severe forms of depression several years into the therapy or even eliminate symptoms entirely. This is the finding of the first long-term study on this form of therapy, conducted by scientists at the Medical Center – University of Freiburg. Seven of the eight patients receiving continuous stimulation in the study showed lasting improvements in their symptoms up to the last observation point four years into treatment. The therapy remained equally effective over the entire period. The scientists prevented minor side-effects from appearing by adjusting the stimulation. The study was published in the journal Brain Stimulation on 1 March 2017.
“Most of the patients respond to the therapy. The remarkable thing is that the effect is also lasting. Other forms of therapy often lose their effectiveness in the course of time. This makes deep brain stimulation a highly promising approach for people with previously non-treatable depression,” says principal investigator Prof. Dr. Thomas Schläpfer, head of the Interventional Biological Psychiatry Unit at the Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy of the Medical Center – University of Freiburg. Deep brain stimulation is a method based on mild electric impulses that can be used to influence selected brain regions with great precision.
Stimulation Takes Effect from the First Month On
The eight test subjects had suffered continuously for three to eleven years from a severe depression that responded neither to drugs nor to psychotherapy or treatments like electroconvulsive therapy. The doctors implanted razor-thin electrodes and stimulated a brain region that is involved in the perception of pleasure and is thus also important for motivation and quality of life. The doctors evaluated the effect of the therapy each month with the help of the established Montgomery-Asberg Rating Scale (MARDS). The patients’ average MARDS score fell from 30 points to 12 points already in the first month and even dropped slightly further by the end of the study. Four patients achieved a MARDS score of less then 10 points, the threshold for diagnosis of depression.
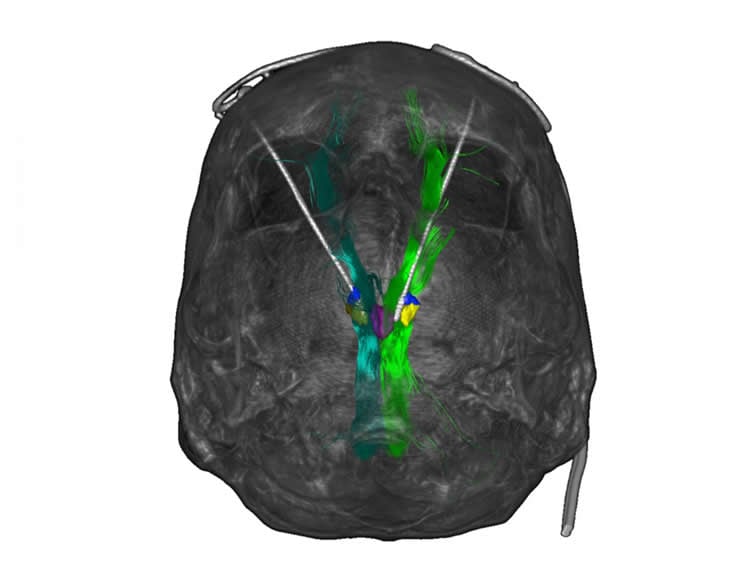
Some of the patients suffered briefly from blurred or double vision. “We managed to alleviate the side effects by reducing the intensity of the stimulation, without diminishing the antidepressant effect of the therapy,” says Prof. Dr. Volker A. Coenen, head of the Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery Unit at the Department of Neurosurgery of the Medical Center – University of Freiburg. The doctors did not observe personality changes, thought disorders, or other side effects in any of the patients.
Larger Follow-Up Study Aims at Registration of Therapy in Europe
If a further five-year study with 50 patients currently underway at the Medical Center – University of Freiburg confirms the effectiveness and safety of the therapy, Prof. Coenen sees the possibility of registering the therapy in Europe. This would allow the therapy to be used outside of studies: “In a few years, deep brain stimulation of this kind could be an effective treatment option for patients with severe depressions,” says Prof. Coenen.
Source: John Wilson – University of Freiburg
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Medical Center – University of Freiburg.
Original Research: Abstract for “Deep brain stimulation to the medial forebrain bundle for depression- long-term outcomes and a novel data analysis strategy” by Bettina H. Bewernick, MSc, PhD, Sarah Kayser, MD, MSc, Sabrina M. Gippert, MSc, Christina Switala, MSc, Volker A. Coenen, MD, and Thomas E. Schlaepfer in Brain Stimulation. Published online February 8 2017 doi:10.1016/j.brs.2017.01.581
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]University of Freiburg “Deep Brain Stimulation Provides Lasting Relief From Severe Depression.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 20 March 2017.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/dbs-depression-6260/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]University of Freiburg (2017, March 20). Deep Brain Stimulation Provides Lasting Relief From Severe Depression. NeuroscienceNew. Retrieved March 20, 2017 from https://neurosciencenews.com/dbs-depression-6260/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]University of Freiburg “Deep Brain Stimulation Provides Lasting Relief From Severe Depression.” https://neurosciencenews.com/dbs-depression-6260/ (accessed March 20, 2017).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Deep brain stimulation to the medial forebrain bundle for depression- long-term outcomes and a novel data analysis strategy
Background
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the supero-lateral branch of the medial forebrain bundle (slMFB) in treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is associated with acute antidepressant effects.
Objective
Long-term clinical effects including changes in quality of life, side effects and cognition as well as long-term data covering four years are assessed.
Methods
Eight TRD patients were treated with DBS bilateral to the slMFB. Primary outcome measure was a 50% reduction in Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) (response) and remission (MADRS <10) at 12 months compared to baseline. Secondary measures were anxiety, general functioning, quality of life, safety and cognition assessed for 4 years. Data is reported as conventional endpoint-analysis and as area under the curve (AUC) timeline analysis.
Results
Six of eight patients (75%) were responders at 12 months, four patients reached remission. Long-term results revealed a stable effect up to four years. Antidepressant efficacy was also reflected in the global assessment of functioning. Main side effect was strabismus at higher stimulation currents. No change in cognition was identified. AUC analysis revealed a significant reduction in depression for 7/8 patients in most months.
Conclusions
Long-term results of slMFB-DBS suggest acute and sustained antidepressant effect; timeline analysis may be an alternative method reflecting patient’s overall gain throughout the study. Being able to induce a rapid and robust antidepressant effect even in a small, sample of TRD patients without significant psychiatric comorbidity, render the slMFB an attractive target for future studies.
“Deep brain stimulation to the medial forebrain bundle for depression- long-term outcomes and a novel data analysis strategy” by Bettina H. Bewernick, MSc, PhD, Sarah Kayser, MD, MSc, Sabrina M. Gippert, MSc, Christina Switala, MSc, Volker A. Coenen, MD, and Thomas E. Schlaepfer in Brain Stimulation. Published online February 8 2017 doi:10.1016/j.brs.2017.01.581