Summary: Wave patterns provide a deeper insight into sleep, consciousness, and attention.
Source: CSHL
While sleeping, the entire brain rolls through long, slow waves of electrical activity, like waves on a calm ocean. Researchers call that state of consciousness “slow wave sleep.” Waking up changes the pattern of electrical activity into something that looks more like random noise. But Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Tatiana Engel, Postdoctoral Fellow Yianling Shi, and their collaborators found there are patterns in the noise.
Looking at the visual processing region of a monkey brain, they discovered smaller, faster, more localized versions of the large rolling sleep waves. The shapes and dynamics of these local waves relate to how attentive that part of the brain is.
The researchers think that the wave patterns provide an important clue to understanding sleep, anesthesia, and attention.
The part of the brain involved in visual processing (the visual cortex) is like a television screen that creates a picture out of a collection of dots or “pixels.” Each brain pixel is composed of a column full of neurons that act together. Unstimulated columns flicker between being electrically active and sensitive to stimuli (“On”) or being inactive and resistant to electrical activity (“Off”). If visual information (a stimulus) hits a visual column that is “On,” then the information is registered as a large electrical spike. But if visual information hits a column when it is “Off,” then it might not be registered at all.
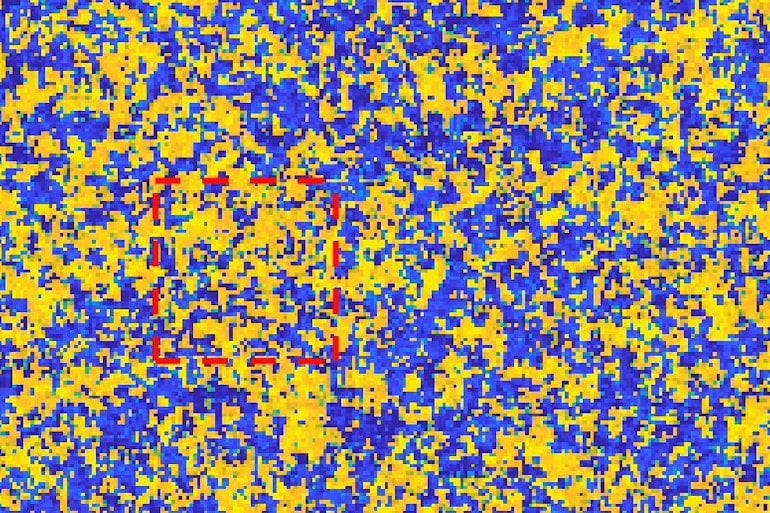
Engel and Shi, in collaboration with Stanford University Professors Kwabena Boahen and Tirin Moore, and University of Washington Assistant Professor Nicholas A. Steinmetz, found that when monkeys are paying attention to a stimulus, the waves get shorter and choppier. “On” and “Off” states blink through visual cortex columns driven by this stimulus more quickly and in a smaller area than when the animal’s attention is elsewhere. But why would an awake and attentive brain want to cycle its columns off and miss information?
Engel has a few hypotheses. She says, “keeping neurons in the ‘On’ state all the time is energetically costly. Another reason is that if we were always receptive to information, we may become overwhelmed; the ‘Off’ state could help suppress irrelevant information.”
The discovery that electrical noise changes patterns with different brain states could help researchers understand brain responses to drugs and disease. And since primate brains are very good at processing visual information, machine learning researchers might borrow its cleverly structured noise tricks to improve artificial brains.
About this neuroscience research news
Author: Press Office
Source: CSHL
Contact: Press Office – CSHL
Image: The image is credited to Yan-Liang Shi/Engel lab/CSHL, 2022
Original Research: Open access.
“Cortical state dynamics and selective attention define the spatial pattern of correlated variability in neocortex” by Yan-Liang Shi et al. Nature Communications
Abstract
Cortical state dynamics and selective attention define the spatial pattern of correlated variability in neocortex
Correlated activity fluctuations in the neocortex influence sensory responses and behavior. Neural correlations reflect anatomical connectivity but also change dynamically with cognitive states such as attention. Yet, the network mechanisms defining the population structure of correlations remain unknown.
We measured correlations within columns in the visual cortex. We show that the magnitude of correlations, their attentional modulation, and dependence on lateral distance are explained by columnar On-Off dynamics, which are synchronous activity fluctuations reflecting cortical state. We developed a network model in which the On-Off dynamics propagate across nearby columns generating spatial correlations with the extent controlled by attentional inputs.
This mechanism, unlike previous proposals, predicts spatially non-uniform changes in correlations during attention. We confirm this prediction in our columnar recordings by showing that in superficial layers the largest changes in correlations occur at intermediate lateral distances.
Our results reveal how spatially structured patterns of correlated variability emerge through interactions of cortical state dynamics, anatomical connectivity, and attention.