Summary: Using the “transport response” method of carrying a crying baby for a few minutes and then sitting with the child helps reduce crying and heart rate.
Source: RIKEN
New research published in Current Biology on September 13 demonstrates the importance of carrying crying infants rather than simply holding them.
Led by Kumi Kuroda at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan, the study details how crying babies are physiologically affected by being held, carried, and laid down.
The data yield a simple but cost-free and effective technique that increases the chance of getting a crying infant to calm down and sleep in bed.
Most parents know the occasional frustration and discomfort of dealing with a crying baby. For some, it’s a regular occurrence that affects the baby’s ability to sleep and stresses out the parents.
What can you do in this situation?
Kuroda and her team found a “Transport Response” in distressed mouse pups and human babies in which infants calm down when carried by their mothers. The response is a complex series of parallel biological processes that result in reduced crying and lower heart rates, which helps parents to transport the infants.
The new study used a baby ECG machine and video cameras to systematically compare changes in heartrate and behavior as mothers acted out activities that are commonly used to calm infants, including carrying, being pushed in a stroller, and holding while sitting.
Data during these activities were recorded from babies that were crying, awake and calm, or sleeping. At each heartbeat, behavior was assessed as asleep, alert, or crying, and scored accordingly. This way the researchers could track changes in both behavior and physiology with sub-second precision.
The experiment led to a few important findings. First, as Kuroda explains, “walking for five minutes promoted sleep, but only for crying infants. Surprisingly, this effect was absent when babies were already calm beforehand.”
Among the babies studied, all had stopped crying by the end of the five-minute walk and had reduced heart rates, and about half were asleep. Second, sitting and holding crying babies was not calming; heart rates tended to go up and crying persisted.
The heartbeat measure allowed the researchers to dissect the effect of each micro-activity as infants were handled. The researchers found that the babies were extremely sensitive to all movements by their mothers.
For example, heartrates went up when mothers turned or when they stopped walking. The most significant event that disturbed the sleeping infants happened just when they became separated from their mothers.
Every mother has experienced the disappointment of having a finally sleeping baby wake up again after being put down. The researchers pinpointed the problem using the heartbeat data. “Although we did not predict it,” says Kuroda, “the key parameter for successful laydown of sleeping infants was the latency from sleep onset.”
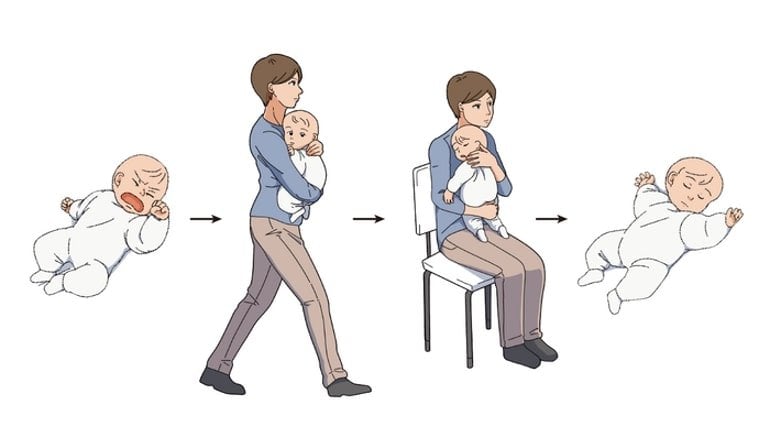
Babies often woke up if they were put down before they got about 8 minutes of sleep. Thus, based on the data, Kuroda recommends that when babies are crying too much and can’t sleep, mothers should carry them steadily for about 5 minutes with few abrupt movements, followed by about 8 minutes of sitting before laying them down for sleep.
Although this procedure does not address why some babies cry excessively and cannot sleep, it offers an immediate solution that can help parents of newborns. Additionally, the researchers recognize the usefulness of heartrate data in this age of wearable fitness devices.
“We are developing a “baby-tech” wearable device with which parents can see the physiological states of their babies on their smartphoness in real-time,” says Kuroda.
“Like science-based fitness training, we can do science-based parenting with these advances, and hopefully help babies to sleep and reduce parental stress caused by excessive infant crying.”
About this parenting research news
Author: Adam Phillips
Source: RIKEN
Contact: Adam Phillips – RIKEN
Image: The image is credited to RIKEN
Original Research: Open access.
“A method to soothe and promote sleep in crying infants utilizing the Transport Response” by Ohmura et al. Current Biology
Abstract
A method to soothe and promote sleep in crying infants utilizing the Transport Response
Highlights
- Infant cry is attenuated by transport, but not by motionless holding
- 5-min transport promotes sleep for crying infants even in the daytime
- Laydown of sleeping infants into a cot either interrupts or deepens infants’ sleep
- Laydown at 5 to 8 min after the sleep onset tends to prevent infant awakening
Summary
Approximately 20%–30% of infants cry excessively and exhibit sleep difficulties for no apparent reason, causing parental stress and even triggering impulsive child maltreatment in a small number of cases.
While several sleep training methods or parental education programs may provide long-term improvement of infant cry and sleep problems, there is yet to be a conclusive recommendation for on-site behavioral interventions.
Previously we have reported that brief carrying of infants transiently reduces infant cry via the transport response, a coordinated set of vagal activation and behavioral calming conserved in altricial mammals.
In this study, we disentangled complex infant responses to maternal holding and transport by combining subsecond-scale, event-locked physiological analyses with dynamic mother-infant interactions. Infant cry was attenuated either by maternal carrying or by reciprocal motion provided by a moving cot, but not by maternal holding.
Five-minute carrying promoted sleep for crying infants even in the daytime when these infants were usually awake, but not for non-crying infants. Maternal laydown of sleeping infants into a cot exerted bimodal effects, either interrupting or deepening the infants’ sleep.
During laydown, sleeping infants were alerted most consistently by the initiation of maternal detachment, then calmed after the completion of maternal detachment in a successful laydown. Finally, the sleep outcome after laydown was associated with the sleep duration before the laydown onset.
These data propose a “5-min carrying, 5- to 8- min sitting” scheme for attending to infant cry and sleep difficulties, which should be further substantiated in future studies.