Summary: Researchers have developed a sensor-instrumented glove for prosthetic hand controls which can sense pressure, temperature, and hydration using electronic chips sending sensory data via a wristwatch.
Source: Purdue University
People with hand amputations experience difficult daily life challenges, often leading to lifelong use of a prosthetic hands and services.
An electronic glove, or e-glove, developed by Purdue University researchers can be worn over a prosthetic hand to provide humanlike softness, warmth, appearance and sensory perception, such as the ability to sense pressure, temperature and hydration. The technology is published in the Aug. 30 edition of NPG Asia Materials.
While a conventional prosthetic hand helps restore mobility, the new e-glove advances the technology by offering the realistic human hand-like features in daily activities and life roles, with the potential to improve their mental health and wellbeing by helping them more naturally integrate into social contexts.
The e-glove uses thin, flexible electronic sensors and miniaturized silicon-based circuit chips on the commercially available nitrile glove. The e-glove is connected to a specially designed wristwatch, allowing for real-time display of sensory data and remote transmission to the user for post-data processing.
Chi Hwan Lee, an assistant professor in Purdue’s College of Engineering, in collaboration with other researchers at Purdue, the University of Georgia and the University of Texas, worked on the development of the e-glove technology.
“We developed a novel concept of the soft-packaged, sensor-instrumented e-glove built on a commercial nitrile glove, allowing it to seamlessly fit on arbitrary hand shapes,” Lee said. “The e-glove is configured with a stretchable form of multimodal sensors to collect various information such as pressure, temperature, humidity and electrophysiological biosignals, while simultaneously providing realistic human hand-like softness, appearance and even warmth.”
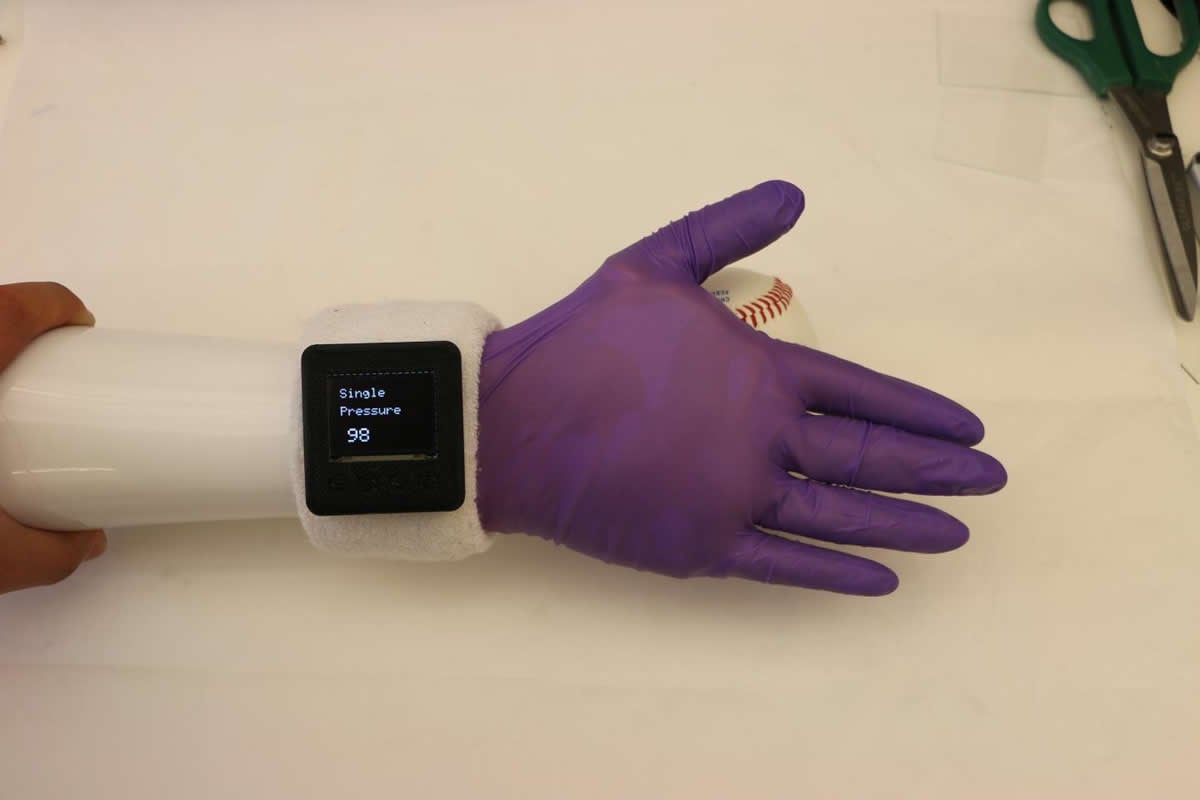
Lee and his team hope that the appearance and capabilities of the e-glove will improve the well-being of prosthetic hand users by allowing them to feel more comfortable in social contexts. The glove is available in different skin tone colors, has lifelike fingerprints and artificial fingernails.
“The prospective end user could be any prosthetic hand users who have felt uncomfortable wearing current prosthetic hands, especially in many social contexts,” Lee said.
The fabrication process of the e-glove is cost-effective and manufacturable in high volume, making it an affordable option for users unlike other emerging technologies with mind, voice and muscle control embedded within the prosthetic at a high cost. Additionally, these emerging technologies do not provide the humanlike features that the e-glove provides.
Credit: Purdue University.
Lee and Min Ku Kim, an engineering doctoral student at Purdue and a co-author on the paper, have worked to patent the technology with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization. The team is seeking partners to collaborate in clinical trials or experts in the prosthetics field to validate the use of the e-glove and to continue optimizing the design of the glove. For more information on licensing a Purdue innovation, contact the Office of Technology Commercialization at [email protected].
“My group is devoted to developing various wearable biomedical devices, and my ultimate goal is to bring these technologies out of the lab and help many people in need. This research represents my continued efforts in this context,” Lee said.
The work aligns with Purdue’s Giant Leaps celebration of the university’s global advancements in health as part of Purdue’s 150th anniversary. That is one of the four themes of the yearlong celebration’s Ideas Festival, designed to showcase Purdue as an intellectual center solving real-world issues.
Source:
Purdue University
Media Contacts:
Chris Adam – Purdue University
Image Source:
The image is credited to Purdue University/Chris Adam.
Original Research: Open access
“Soft-packaged sensory glove system for human-like natural interaction and control of prosthetic hands”. Min Ku Kim, Ramviyas Nattanmai Parasuraman, Liu Wang, Yeonsoo Park, Bongjoong Kim, Seung Jun Lee, Nanshu Lu, Byung-Cheol Min & Chi Hwan Lee.
NPG Asia Materials 10.1038/s41427-019-0143-9
Abstract
Soft-packaged sensory glove system for human-like natural interaction and control of prosthetic hands
People with hand amputations experience strenuous daily life challenges, often leading to lifelong use of a prosthetic hand(s) and services. Modern advanced prosthetic hands must be able to provide human hand-like sensory perceptions to receive external stimuli during daily activities while simultaneously replicating a realistic appearance and physical properties to naturally integrate in social contexts; however, the practical realization of these issues are impeded by a lack of effective methodologies. Herein, we present an optimal set of materials, design layouts, and fabrication schemes to construct an easy-to-wear seamless electronic glove (e-glove) suitable for arbitrary hand shapes that provides all of the desired human hand-like features. The system configuration involves a connection to a control wristwatch unit for real-time display of sensory data measured and remote transmission to the user. The experimental and computational studies provide details regarding the underlying principles of the materials selection, mechanics design, and operational management of the entire system. The demonstration of the e-glove system in interactions with human subjects illustrates the utility, comfort, and convenience of this device.