Summary: Researchers have created a collection of month-to-month infant brain maps that capture the fine detail of changes in the early developing brain.
Source: UNC
Human brain atlases can be used by medical professionals to track normative trends over time and to pinpoint crucial aspects of early brain development.
With these atlases, they are able to see what typical structural and functional development looks like, making it easier for them to spot the symptoms of abnormal development, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, and cerebral palsy.
Pew-Thian Yap, Ph.D., professor in the UNC Department of Radiology, and colleagues in the department and the Biomedical Research Imaging Center (BRIC) have created a new collection of month-by-month infant brain atlas (IBA) that capture fine spatiotemporal details of the early developing brain.
In this work, published in the journal Nature Methods, the scientists created a set of month-specific surface-volume longitudinal brain atlases of infants from 2 weeks to 2 years of age. Sahar Ahmad, Ph.D., research instructor of radiology, was lead author on the paper.
“Brain atlases are key to understanding neurodevelopment through the lenses of cellular composition, neural pathways, and functional organization,” Yap said.
“The human brain atlases created by our team depict the early development phase of postnatal neurodevelopment. Our atlases will be a resource valuable to brain scientists in unraveling key normative and aberrant traits of, arguably, the most important phase of human brain development.”
Throughout the first two years of life, the human brain undergoes a whole range of cellular processes that drive the rapid growth of the infant brain. It is during this period that the brain changes structurally and reorganizes its neural circuits. When development goes awry, it can have detrimental effects on the quality of life, including heightened risk for autism, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
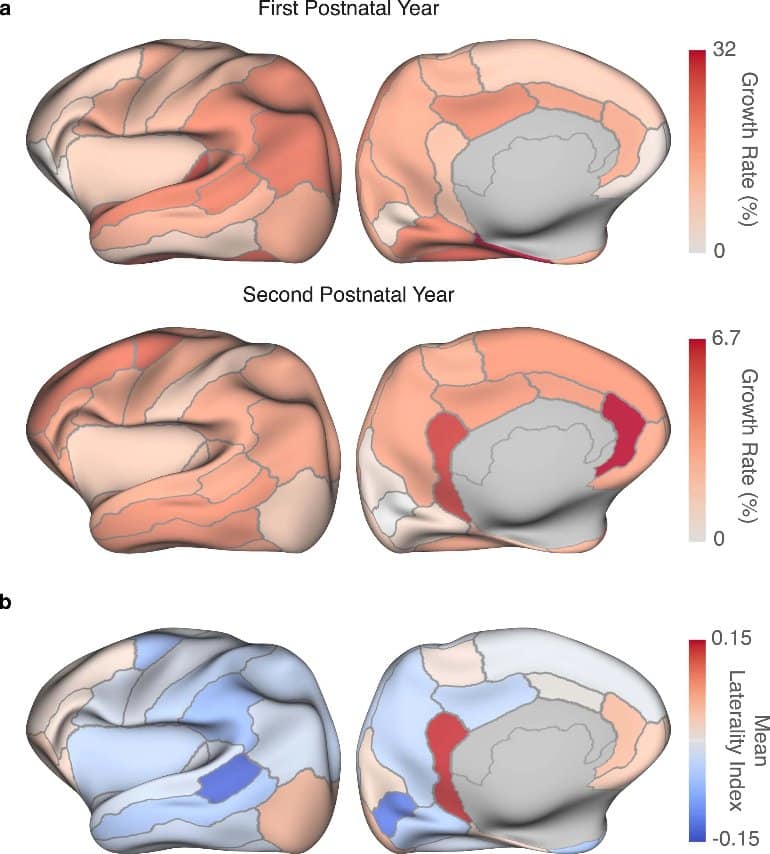
By using the IBA, researchers are able to capture changes in brain structure, cortical geometry, and tissue contrast.
The atlases also revealed that cortices in the temporal, parietal, and prefrontal regions of the brain are thicker than the primary visual and sensorimotor cortices. This is consistent with the finding that the higher-order functions of the infant brain—such as attention, working memory, inhibition, and problem-solving—mature more slowly than the areas of the brain that are responsible for the visual, motor, and sensory functions.
Overall, the surface-volume consistent IBA accurately captures the infant growth trajectories and does so with rich anatomical details. These atlases recorded the monthly changes in the normally developing brains’ size, shape, and cortical geometry as well as their tissue contrast, volume, and microstructural characteristics from 2 weeks to 2 years of age.
“We hope that these atlases will become a common coordinate framework to facilitate the discovery of new insights into developmental processes underpinning child cognition and social behavior,” Yap said.
About this brain mapping research news
Author: Press Office
Source: UNC
Contact: Press Office – UNC
Image: The image is credited to the researchers
Original Research: Open access.
“Multifaceted atlases of the human brain in its infancy” by Sahar Ahmad et al. Nature Medicine
Abstract
Multifaceted atlases of the human brain in its infancy
Brain atlases are spatial references for integrating, processing, and analyzing brain features gathered from different individuals, sources, and scales.
Here we introduce a collection of joint surface–volume atlases that chart postnatal development of the human brain in a spatiotemporally dense manner from two weeks to two years of age.
Our month-specific atlases chart normative patterns and capture key traits of early brain development and are therefore conducive to identifying aberrations from normal developmental trajectories.
These atlases will enhance our understanding of early structural and functional development by facilitating the mapping of diverse features of the infant brain to a common reference frame for precise multifaceted quantification of cortical and subcortical changes.