Summary: Using machine learning to analyze fMRI brain scans of grieving people, researchers shed light on how unconscious suppression occurs.
Source: Columbia University.
People who are grieving a major loss, such as the death of a spouse or a child, use different coping mechanisms to carry on with their lives. Psychologists have been able to track different approaches, which can reflect different clinical outcomes. One approach that is not usually successful is avoidant grief, a state in which people suffering from grief show marked, effortful, repeated, and often unsuccessful attempts to stop themselves from thinking about their loss. While researchers have shown that avoidant grievers consciously monitor their external environment in order to avoid reminders of their loss, no one has yet been able to show whether these grievers also monitor their mental state unconsciously, trying to block any thoughts of loss from rising to their conscious state.
A new collaborative study between Columbia Engineering and Columbia University Irving Medical Center published online December 7 in SCAN: Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience demonstrates that avoidant grievers do unconsciously monitor and block the contents of their mind-wandering, a discovery that could lead to more effective psychiatric treatment for bereaved people. The researchers, who studied 29 bereaved subjects, are the first to show how this unconscious thought suppression occurs. They tracked ongoing processes of mental control as loss-related thoughts came in and out of conscious awareness during a 10-minute period of mind-wandering.
Co-directed by Paul Sajda, professor of biomedical engineering, electrical engineering, and radiology, and John J. Mann, Paul Janssen Professor of Translational Neuroscience (in Psychiatry and in Radiology), the researchers used a new approach to track the interactions between mental processes: a machine-learning approach to functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) called “neural decoding,” which establishes a neural pattern or fingerprint that can be used to determine when a given mental process is happening.
“The major challenge of our study was to be able ‘look under the hood’ of a person’s natural mind-wandering state to see what underlying processes were actually controlling their experience,” says Noam Schneck, lead author of the study, a postdoctoral fellow in Sajda’s lab and now assistant professor of clinical medical psychology (in psychiatry) at Columbia University Department of Psychiatry/ New York State Psychiatric Institute. “No one has done this kind of work before, showing this type of consistent control of one mental process–thinking about loss–by another–selective attention–as it happens spontaneously and unconsciously. These findings are significant because they open the door to building a fuller picture of the unconscious mind. We know that the experiences we have arise as a combination of constantly interacting networks. Now we have shown this interaction as it happens naturalistically as well as the way it controls experiences.”
The team recorded fMRI from people who had lost a first-degree relative (a spouse or partner) within the last 14 months. The subjects performed a modified Stroop task, a test widely used in psychology to measure a person’s ability to control the contents of attention, and a separate task presenting pictures and stories of the deceased. Using machine learning, the team then trained respective neural fingerprints for attentional control based on the Stroop task and mental representation of the deceased based on the pictures and stories. The team observed spontaneous fluctuations in these processes that occurred during a neutral mind-wandering fMRI task. They discovered that those with more avoidant grief engaged their attentional control process to block representations of the deceased from conscious awareness.
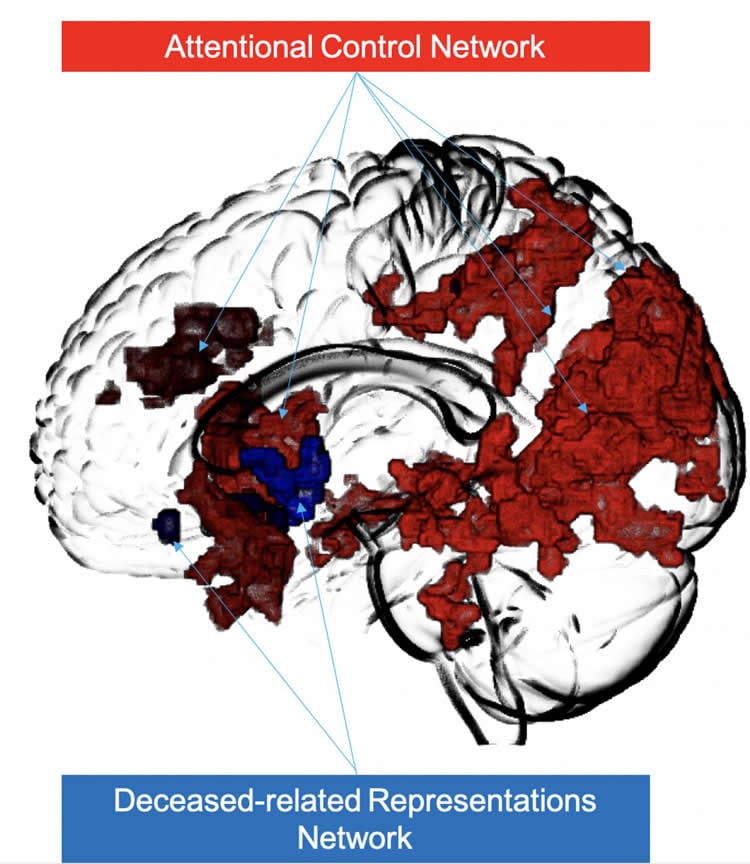
“Our findings show that avoidant grief involves attentional control to reduce the likelihood that deceased-related representations reach full conscious awareness,” says Schneck. “Even though they are not aware of it, avoidant grievers actively control their mental state so that spontaneous thoughts of loss do not enter their consciousness. This kind of tailoring of mind-wandering likely exhausts mental energy and leads to time periods when the thoughts actually do break through. It is like an ineffective pop-up blocker that runs in the background of your computer. You might not be aware that it’s there but it slows down the overall operating speed and eventually breaks down and the pop ups get through.”
The researchers suggest that one treatment goal for avoidant grievers may be to relax the conscious and unconscious mental controls that they maintain over their thinking of the loss. Since this control and monitoring happens outside of conscious awareness, this would be challenging to do, but training in mindfulness and acceptance may help some people relax both their conscious and unconscious mental controls.
“This research approach is an innovative collaboration between engineering and psychiatry that optimizes the tools of engineering to address critical questions in psychiatry,” says Sajda, who is also a member of Columbia’s Data Science Institute. “What we’ve shown in this paper is that outside of our conscious awareness, we are constantly editing our own mental experiences to control what does and does not get in. And this process of editing is not always helpful.”
The researchers are now planning a longitudinal study to see if avoidant grievers’ internal vigilance might predict poor grief outcomes over the long term.
Funding: The study was funded by a Distinguished Investigator Grant (DIG-0-163-12) (JJM) and a Young Investigator Grant (YIG-0-215-13) (NS) from the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. NS was supported by a National Institute of Mental Health T32 Training Grant in Anxiety and Related Disorders.
Financial Disclosures: Dr. Mann receives royalties for commercial use of the C-SSRS from the Research Foundation for Mental Hygiene and has stock options in Qualitas Health, a start- up developing a PUFA supplement. Dr. Sajda is the majority owner and Chairman of the Board of Neuromatters LLC, a brain computer interface neuromarketing and gaming company. Dr. Galfalvy’s family owns stock in Illumina, Inc. Dr. Schneck, Dr. Bonnano, Dr. Ochsner, Dr. Haufe and Mr. Tu have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Source: Holly Evarts – Columbia University
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Noam Schneck/Columbia Engineering.
Original Research: Open access research for “Ongoing Monitoring of Mindwandering in Avoidant Grief Through Cortico-Basal-Ganglia Interactions” by Noam Schneck, Tao Tu, Stefan Haufe, George A Bonanno, Hanga GalfaIvy, Kevin Ochsner, J John Mann, and Paul Sajda in Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. Published December 6 2018.
doi:10.1093/scan/nsy114
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]Columbia University”Editing Consciousness: How Bereaved People Control Their Thoughts Without Knowing It.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 10 December 2018.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/consciousness-bereaved-people-10317/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]Columbia University(2018, December 10). Editing Consciousness: How Bereaved People Control Their Thoughts Without Knowing It. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved December 10, 2018 from https://neurosciencenews.com/consciousness-bereaved-people-10317/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]Columbia University”Editing Consciousness: How Bereaved People Control Their Thoughts Without Knowing It.” https://neurosciencenews.com/consciousness-bereaved-people-10317/ (accessed December 10, 2018).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Ongoing Monitoring of Mindwandering in Avoidant Grief Through Cortico-Basal-Ganglia Interactions
An avoidant grief style is marked by repeated and often unsuccessful attempts to prevent thinking about loss. Prior work shows avoidant grief involves monitoring the external environment in order to avoid reminders of the loss. Here we sought to determine whether avoidant grievers also monitor the internal environment in attempts to minimize conscious awareness of loss-related thoughts. Individuals bereaved of a first-degree relative, spouse or partner within the last 14 months participated in an fMRI study (N=29). We first applied machine learning to train neural patterns for attentional control and representation of the deceased (N=23). The attentional pattern was trained using fMRI data from a modified Stroop task assessing selective attention to reminders of the deceased. The representational pattern was trained using fMRI data from a task presenting pictures and stories of the deceased. We observed spontaneous fluctuations in these processes occurring during a neutral mindwandering fMRI task (N=27). At higher levels of avoidant grieving, activation of attentional control disrupted the relationship between the representational process and thoughts of loss. These findings show that avoidant grief involves attentional control to reduce the likelihood that deceased-related representations reach full conscious awareness.