Improves potential to help Parkinson’s, other degenerative diseases.
National Institutes of Health-funded scientists have developed a 3D micro-scaffold technology that promotes reprogramming of stem cells into neurons, and supports growth of neuronal connections capable of transmitting electrical signals. The injection of these networks of functioning human neural cells — compared to injecting individual cells — dramatically improved their survival following transplantation into mouse brains. This is a promising new platform that could make transplantation of neurons a viable treatment for a broad range of human neurodegenerative disorders.
Previously, transplantation of neurons to treat neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, had very limited success due to poor survival of neurons that were injected as a solution of individual cells. The new research is supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), part of NIH.
“Working together, the stem cell biologists and the biomaterials experts developed a system capable of shuttling neural cells through the demanding journey of transplantation and engraftment into host brain tissue,” said Rosemarie Hunziker, Ph.D., director of the NIBIB Program in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. “This exciting work was made possible by the close collaboration of experts in a wide range of disciplines.”
The research was performed by researchers from Rutgers University, Piscataway, New Jersey, departments of Biomedical Engineering, Neuroscience and Cell Biology, Chemical and Biochemical Engineering, and the Child Health Institute; Stanford University School of Medicine’s Institute of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, Stanford, California; the Human Genetics Institute of New Jersey, Piscataway; and the New Jersey Center for Biomaterials, Piscataway. The results are reported in the March 17, 2016 issue of Nature Communications.
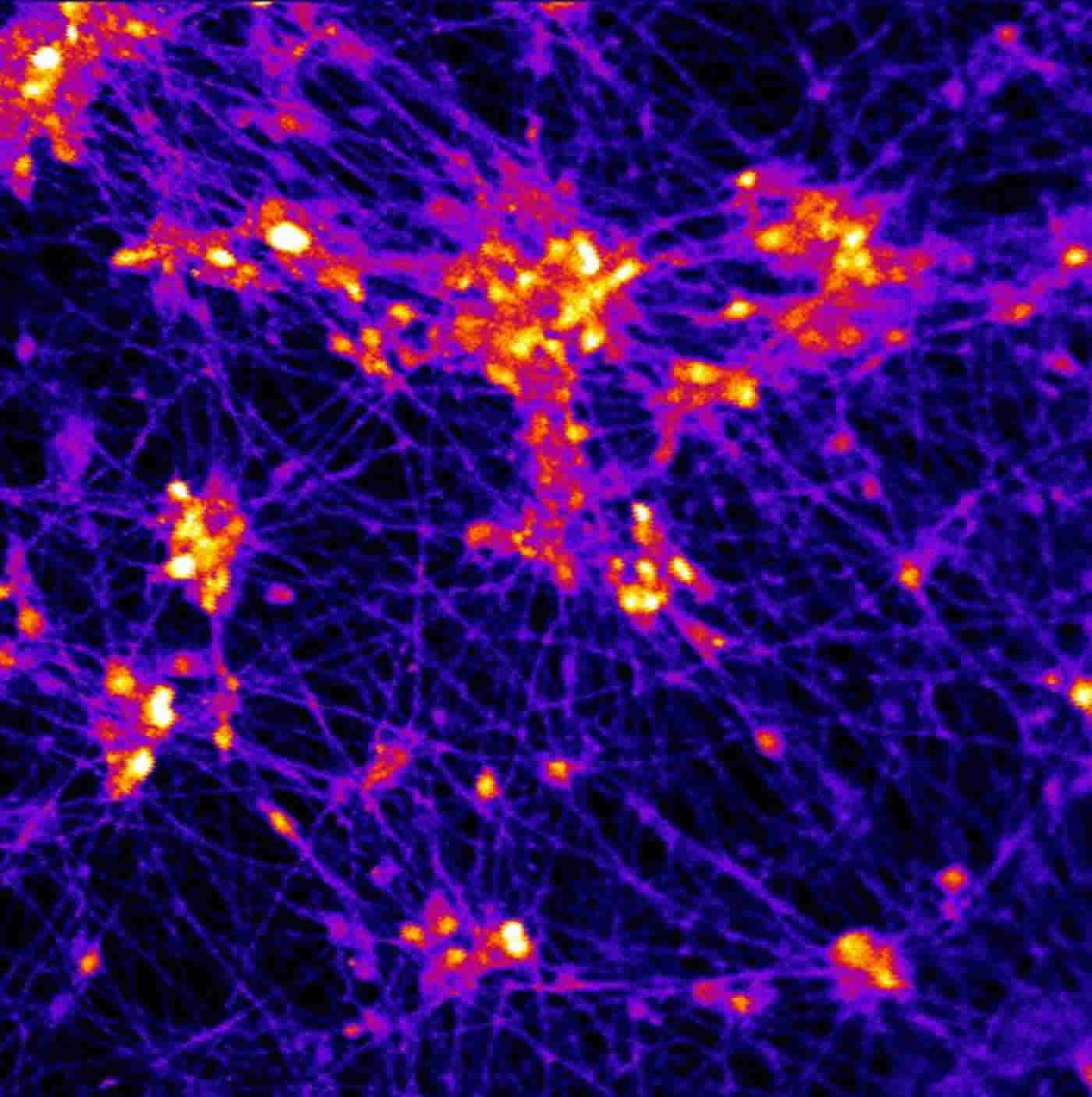
The researchers experimented in creating scaffolds made of different types of polymer fibers, and of varying thickness and density. They ultimately created a web of relatively thick fibers using a polymer that stem cells successfully adhered to. The stem cells used were human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which can be readily generated from adult cell types such as skin cells. The iPSCs were induced to differentiate into neural cells by introducing the protein NeuroD1 into the cells.
The space between the polymer fibers turned out to be critical. “If the scaffolds were too dense, the stem cell-derived neurons were unable to integrate into the scaffold, whereas if they are too sparse then the network organization tends to be poor,” explained Prabhas Moghe, Ph.D., distinguished professor of biomedical engineering & chemical engineering at Rutgers University and co-senior author of the paper. “The optimal pore size was one that was large enough for the cells to populate the scaffold but small enough that the differentiating neurons sensed the presence of their neighbors and produced outgrowths resulting in cell-to-cell contact. This contact enhances cell survival and development into functional neurons able to transmit an electrical signal across the developing neural network.”
To test the viability of neuron-seeded scaffolds when transplanted, the researchers created micro-scaffolds that were small enough for injection into mouse brain tissue using a standard hypodermic needle. They injected scaffolds carrying the human neurons into brain slices from mice and compared them to human neurons injected as individual, dissociated cells.
The neurons on the scaffolds had dramatically increased cell-survival compared with the individual cell suspensions. The scaffolds also promoted improved neuronal outgrowth and electrical activity. Neurons injected individually in suspension resulted in very few cells surviving the transplant procedure.
Human neurons on scaffolds compared to neurons in solution were then tested when injected into the brains of live mice. Similar to the results in the brain slices, the survival rate of neurons on the scaffold network was increased nearly 40-fold compared to injected isolated cells. A critical finding was that the neurons on the micro-scaffolds expressed proteins that are involved in the growth and maturation of neural synapses–a good indication that the transplanted neurons were capable of functionally integrating into the host brain tissue.
The success of the study gives this interdisciplinary group reason to believe that their combined areas of expertise have resulted in a system with much promise for eventual treatment of human neurodegenerative disorders. In fact, they are now refining their system for specific use as an eventual transplant therapy for Parkinson’s disease. The plan is to develop methods to differentiate the stem cells into neurons that produce dopamine, the specific neuron type that degenerates in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. The work also will include fine-tuning the scaffold materials, mechanics and dimensions to optimize the survival and function of dopamine-producing neurons, and finding the best mouse models of the disease to test this Parkinson’s-specific therapy.
Funding: The NIH supported the study through grants EB001046 and EB005583 from NIBIB; grant NS051401 from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; grants AA024033 and AA023797 from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism; and grants DA035594 and DA03968 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Source: Thomas Johnson – NIBIB/NIH
Image Credit: The image is credited to Prabhas Moghe, Rutgers.
Original Research: Full open access research for “Generation and transplantation of reprogrammed human neurons in the brain using 3D microtopographic scaffolds” by Aaron L. Carlson, Neal K. Bennett, Nicola L. Francis, Apoorva Halikere, Stephen Clarke, Jennifer C. Moore, Ronald P. Hart, Kenneth Paradiso, Marius Wernig, Joachim Kohn, Zhiping P. Pang, and Prabhas V. Moghe in Nature Communications. Published online March 17 2016 doi:10.1038/ncomms10862
Abstract
Generation and transplantation of reprogrammed human neurons in the brain using 3D microtopographic scaffolds
Cell replacement therapy with human pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons has the potential to ameliorate neurodegenerative dysfunction and central nervous system injuries, but reprogrammed neurons are dissociated and spatially disorganized during transplantation, rendering poor cell survival, functionality and engraftment in vivo. Here, we present the design of three-dimensional (3D) microtopographic scaffolds, using tunable electrospun microfibrous polymeric substrates that promote in situ stem cell neuronal reprogramming, neural network establishment and support neuronal engraftment into the brain. Scaffold-supported, reprogrammed neuronal networks were successfully grafted into organotypic hippocampal brain slices, showing an ~3.5-fold improvement in neurite outgrowth and increased action potential firing relative to injected isolated cells. Transplantation of scaffold-supported neuronal networks into mouse brain striatum improved survival ~38-fold at the injection site relative to injected isolated cells, and allowed delivery of multiple neuronal subtypes. Thus, 3D microscale biomaterials represent a promising platform for the transplantation of therapeutic human neurons with broad neuro-regenerative relevance.
“Generation and transplantation of reprogrammed human neurons in the brain using 3D microtopographic scaffolds” by Aaron L. Carlson, Neal K. Bennett, Nicola L. Francis, Apoorva Halikere, Stephen Clarke, Jennifer C. Moore, Ronald P. Hart, Kenneth Paradiso, Marius Wernig, Joachim Kohn, Zhiping P. Pang, and Prabhas V. Moghe in Nature Communications. Published online March 17 2016 doi:10.1038/ncomms10862






