Summary: A new study reports believing a cigarette contains nicotine satisfied a smoker’s cravings.
Source: Virginia Tech.
Virginia Tech, University of Texas-Dallas scientists shed light on belief-drug interactions.
Craving relief may depend more on the belief of satisfaction than actual relief, according to scientists at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute and the Center for BrainHealth at The University of Texas at Dallas.
In a study published in Frontiers in Psychiatry, researchers found that participants failed to satisfy their craving by simply smoking a nicotine cigarette. The participants had to actually believe that the cigarette contained nicotine.
“We expected the presence of nicotine to show some sort of craving response compared to conditions where the subjects did not receive nicotine despite the belief about the nicotine given, but that was not what we found,” said Read Montague, co-author of the study, director of the Human Neuroimaging Laboratory and the Computational Psychiatry Unit at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute. Montague is also the inaugural Virginia Tech Carilion Vernon Mountcastle Research Professor.
Montague and his team used functional magnetic resonance imaging to capture neural activity, with a specific focus on the insula cortex. This brain region plays a role in diverse functions, such as bodily perception and self-awareness.
“We examined the impact of beliefs about cravings prior to and after smoking while also measuring neural activity,” said Xiaosi Gu, an assistant professor at the University of Texas at Dallas, head of the Computational Psychiatry Unit at the Center for BrainHealth, and the study’s co-author. “We focused on neural activity in the insula cortex, one of the key brain areas associated with drug craving and addiction.”
The study had 24 participants, all of whom were chronic smokers between the ages of 30 and 50 years old. Each participant visited the laboratory on four separate occasions, after avoiding nicotine cigarettes from midnight the night before.
On every visit, the participants smoked a cigarette and then underwent an fMRI scan while playing a decision making game. Each of the four visits tested a different condition: participants believed the cigarettes contained nicotine, but received a placebo; or they believed the cigarette was nicotine-free and received a nicotine cigarette; or they believed the cigarette contained nicotine and received a nicotine cigarette; or they believed the cigarette was nicotine free and they received a placebo. Before smoking the cigarette and after the task, participants rated their craving levels.
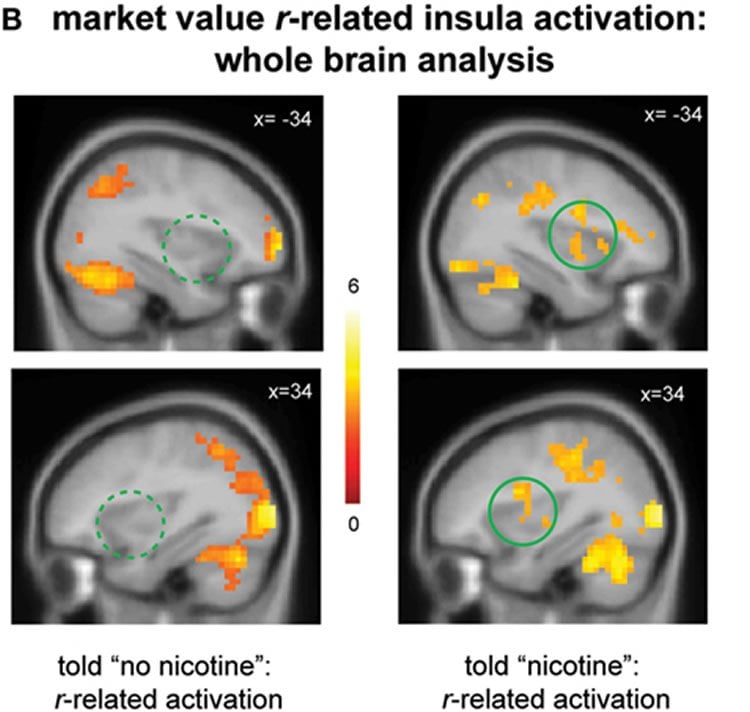
The scans showed a significant neural activation that correlated with both craving and learning signals when participants smoked a nicotine cigarette and also believed it contained nicotine. But, smoking a nicotine cigarette while believing it was a placebo did not produce the same brain signals.
“These results suggest that for drugs to have an effect on a person, he or she needs to believe that the drug is present,” Gu said.
This study’s results extend the researchers’ previous findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that beliefs about nicotine could modulate decision making and accompanying neural signals.
“Our research group continues to provide evidence that beliefs can be as powerful a physical influence on the brain as neuroactive drugs,” Montague said, pointing to this relationship as a potential therapeutic target to battle addiction. “Maybe we can engineer belief states to better effect behavior change in addiction.”
Funding: Study funded by National Institutes of Health, Kane Family Foundation, Wellcome Trust, Dallas Foundation.
Source: Ashley WennersHerron – Virginia Tech
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to the researchers/Frontiers in Psychiatry.
Original Research: Full open access research for “Belief about Nicotine Modulates Subjective Craving and Insula Activity in Deprived Smokers” by Xiaosi Gu, Terry Lohrenz, Ramiro Salas, Philip R. Baldwin, Alireza Soltani, Ulrich Kirk, Paul M. Cinciripini, and P. Read Montague in Frontiers in Psychiatry. Published online July 13 2016 doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00126
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]Virginia Tech. “Belief About Nicotine Level Influences Cigarette Cravings and Brain Activity.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 13 September 2016.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/cravings-nicotine-levels-5029/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]Virginia Tech. (2016, September 13). Belief About Nicotine Level Influences Cigarette Cravings and Brain Activity. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved September 13, 2016 from https://neurosciencenews.com/cravings-nicotine-levels-5029/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]Virginia Tech. “Belief About Nicotine Level Influences Cigarette Cravings and Brain Activity.” https://neurosciencenews.com/cravings-nicotine-levels-5029/ (accessed September 13, 2016).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Belief about Nicotine Modulates Subjective Craving and Insula Activity in Deprived Smokers
Little is known about the specific neural mechanisms through which cognitive factors influence craving and associated brain responses, despite the initial success of cognitive therapies in treating drug addiction. In this study, we investigated how cognitive factors such as beliefs influence subjective craving and neural activities in nicotine-addicted individuals using model-based functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and neuropharmacology. Deprived smokers (N = 24) participated in a two-by-two balanced placebo design, which crossed beliefs about nicotine (told “nicotine” vs. told “no nicotine”) with the nicotine content in a cigarette (nicotine vs. placebo) which participants smoked immediately before performing a fMRI task involving reward learning. Subjects’ reported craving was measured both before smoking and after the fMRI session. We found that first, in the presence of nicotine, smokers demonstrated significantly reduced craving after smoking when told “nicotine in cigarette” but showed no change in craving when told “no nicotine.” Second, neural activity in the insular cortex related to craving was only significant when smokers were told “nicotine” but not when told “no nicotine.” Both effects were absent in the placebo condition. Third, insula activation related to computational learning signals was modulated by belief about nicotine regardless of nicotine’s presence. These results suggest that belief about nicotine has a strong impact on subjective craving and insula responses related to both craving and learning in deprived smokers, providing insights into the complex nature of belief–drug interactions.
“Belief about Nicotine Modulates Subjective Craving and Insula Activity in Deprived Smokers” by Xiaosi Gu, Terry Lohrenz, Ramiro Salas, Philip R. Baldwin, Alireza Soltani, Ulrich Kirk, Paul M. Cinciripini, and P. Read Montague in Frontiers in Psychiatry. Published online July 13 2016 doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00126