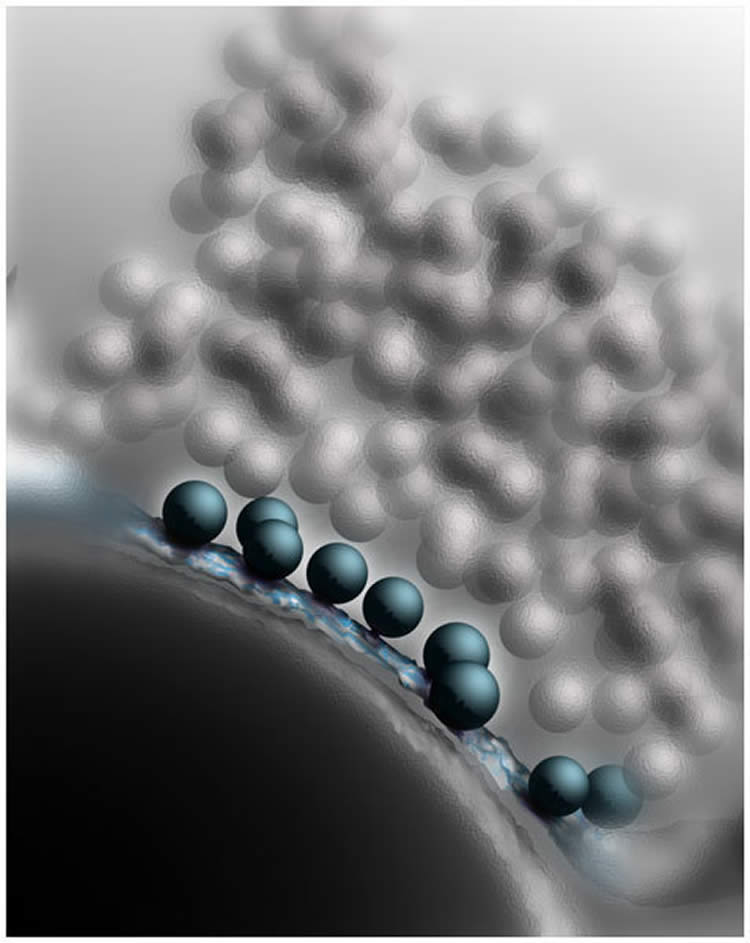
Vesicles filled with neurotransmitters touch the cell membrane, thereby enabling their rapid-fire release.
While neurons rapidly propagate information in their interior via electrical signals, they communicate with each other at special contact points known as the synapses. Chemical messenger substances, the neurotransmitters, are stored in vesicles at the synapses. When a synapse becomes active, some of these vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents. To ensure that valuable time is not lost, synapses always have some readily releasable vesicles on standby. With the help of high-resolution, three-dimensional electron microscopy, scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine in Göttingen succeeded in demonstrating that these fusionable vesicles have a very special characteristic: they already have close contact with the cell membrane long before the actual fusion occurs. In addition, the research team also decoded the molecular machinery that facilitates the operation of this docking mechanism.
The fusion of the neurotransmitter vesicles with the cell membrane involves close cooperation between numerous protein components, which monitor each other and ensure that every single ‘participant’ is always in the right place. This is referred to as the fusion machinery and the comparison is an apt one: if a cogwheel in a clock mechanism is broken, the hands do not move. In a similar way, faulty or missing molecules impair synaptic operations.
In research studies carried out some years ago, Nils Brose and his colleague JeongSeop Rhee from the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine in Göttingen already demonstrated that the transmission of information at the synapses in genetically modified mice, in which all known genes of the Munc13 or CAPS proteins had been switched off, is severely defective. Although the neurons of the genetically modified mice do not differ from those of healthy mice when examined under an optical microscope, if Munc13 is missing, the release of neurotransmitters actually grinds to a halt completely. Brose and Rhee’s findings showed that to be able to react immediately to signals at all times, each synapse must keep a small number of ‘readily releasable’ fusionable vesicles on standby.
But how do Munc13 and CAPS convert the vesicles to this kind of fusionable state? To answer this question, the Göttingen-based scientists studied the synaptic contacts in the minutest possible detail. To do this, neurobiologists Cordelia Imig and Ben Cooper, who have been working with Brose and Rhee for many years, used a high-pressure freezing process. This involves the rapid freezing of neurons in the brain tissue under high pressure so that no disruptive ice crystals are formed and the fine structure of the cells is particularly well conserved. The samples obtained in this way were then analysed using electron tomography. Using this method, electron microscope images of a structure are recorded from many different angles, in a similar way to the process used in medical computed tomography. The individual images can then be combined on the computer to give a high-resolution three-dimensional image – of a synapse in this case (see image).
“Our results showed that readily releasable vesicles in healthy synapses touch the cell membrane,” explains Cooper. “However, if Munc13 and CAPS proteins are missing, the vesicles do not reach the active zone and accumulate a few nanometres away from it.” To their astonishment, the researchers also observed that SNARE proteins, which collaborate with Munc13 and CAPS in the nerve endings, are also involved in this docking process. SNARE proteins are found in the cell and vesicle membranes of healthy synapses and control the fusion of the two membranes during neurotransmitter release. When a vesicle approaches the cell membrane, the individual SNARE molecules line up opposite each other like the sides of a zip and pull the membranes close to each other in this way. The vesicles await the starting gun for their fusion in this state – in the starting blocks, so to speak.
The findings of the neurobiologists in Göttingen prove that Munc13, CAPS and SNARE proteins closely align the vesicle and cell membrane in the synapse, long before the signal for fusion is given. This is the only way that the fast and controlled transmission of information at the synapse can be guaranteed, thanks to which we can react specifically to information from our environment. “It had long been clear that synapses have to be extremely fast to carry out all of the many complex brain functions. Our study shows for the first time how this is managed at the molecular level and on the level of the synaptic vesicles,” says Brose. Because almost all of the protein components involved in this process also play a role in neurological and psychiatric diseases, the Göttingen-based scientists believe that their discovery will soon benefit medical research.
Other contributors to the paper were Paul J. Adams, Manu Ben-Johny, Ivy E. Dick and Takanari Inoue, all of The Johns Hopkins University.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (grant numbers R01NS085074 and R01NS073874), the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (grant number R37HL076795), the National Institute of Mental Health (grant number F31MH88109) and Parkinson Society Canada.
Contact: Prof. Dr. Nils Brose – Max Planck Institute
Source: Max Planck Institute press release
Image Source: The image is credited to Benjamin H. Cooper and is adapted from the Max Planck Institute press release
Original Research: Abstract for “The morphological and molecular nature of synaptic vesicle priming at presynaptic active zones” by Imig, C., Min, S.-W., Krinner, S., Arancillo, M., Rosenmund, C., Südhof, T.C., Rhee, J.-S., Brose, N. and Cooper, B.H in Neuron. Published online October 23 2014 doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.10.009