Summary: A lack of sleep impairs our basic social conscience, making us less willing to help others.
Source: UC Berkeley
Humans help each other—it’s one of the foundations of civilized society. But a new study by scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, reveals that a lack of sleep blunts this fundamental human attribute, with real-world consequences.
Lack of sleep is known to be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, depression, diabetes, hypertension and overall mortality. However, these new discoveries show that a lack of sleep also impairs our basic social conscience, making us withdraw our desire and willingness to help other people.
In one portion of the new study, the scientists showed that charitable giving in the week after the beginning of Daylight Saving Time, when residents of most states “spring forward” and lose one hour of their day, dropped by 10%—a decrease not seen in states that do not change their clocks or when states return to standard time in the fall.
The study, led by UC Berkeley research scientist Eti Ben Simon and Matthew Walker, a UC Berkeley professor of psychology, adds to a growing body of evidence demonstrating that inadequate sleep not only harms the mental and physical well-being of an individual, but also compromises the bonds between individuals—and even the altruistic sentiment of an entire nation.
“Over the past 20 years, we have discovered a very intimate link between our sleep health and our mental health. Indeed, we’ve not been able to discover a single major psychiatric condition in which sleep is normal,” Walker said.
“But this new work demonstrates that a lack of sleep not only damages the health of an individual, but degrades social interactions between individuals and, furthermore, degrades the very fabric of human society itself. How we operate as a social species—and we are a social species—seems profoundly dependent on how much sleep we are getting.”
“We’re starting to see more and more studies, including this one, where the effects of sleep loss don’t just stop at the individual, but propagate to those around us,” said Ben Simon.
“If you’re not getting enough sleep, it doesn’t just hurt your own well-being, it hurts the well-being of your entire social circle, including strangers.”
Ben Simon, Walker and colleagues Raphael Vallat and Aubrey Rossi will publish their results August 23 in the open access journal PLOS Biology. Walker is the director of the Center for Human Sleep Science. He and Ben Simon are members of the Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute at UC Berkeley.
Sleeplessness dampens theory of mind network
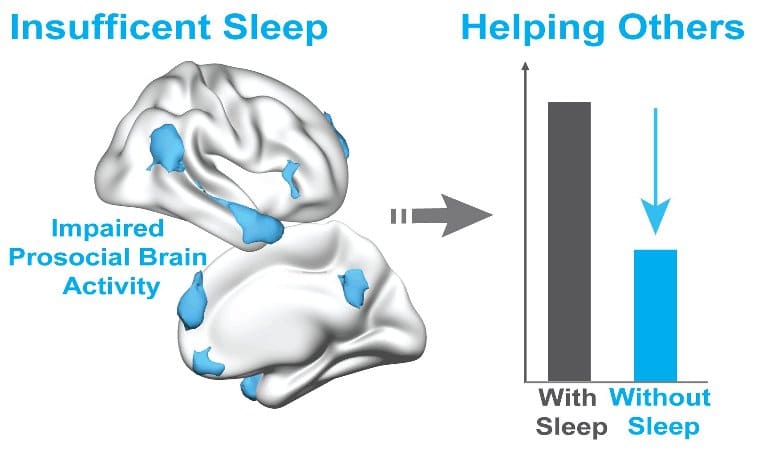
The new report describes three separate studies that assessed the impact of sleep loss on people’s willingness to help others. In the first study, the scientists placed 24 healthy volunteers in a functional magnetic resonance imager (fMRI) to scan their brains after eight hours of sleep and after a night of no sleep.
They found that areas of the brain that form the theory of mind network, which is engaged when people empathize with others or try to understand other people’s wants and needs, were less active after a sleepless night.
“When we think about other people, this network engages and allows us to comprehend what other person’s needs are: What are they thinking about? Are they in pain? Do they need help?” Ben Simon said.
“However, this network was markedly impaired when individuals were sleep deprived. It’s as though these parts of the brain fail to respond when we are trying to interact with other people after not getting enough sleep.”
In a second study, they tracked more than 100 people online over three or four nights. During this time, the researchers measured the quality of their sleep—how long they slept, how many times they woke up—and then assessed their desire to help others, such as holding an elevator door open for someone else, volunteering or helping an injured stranger on the street.
“Here, we found that a decrease in the quality of someone’s sleep from one night to the next predicted a significant decrease in the desire to help other people from one subsequent day to the next,” Ben Simon said.
“Those with poor sleep the night prior were the ones that reported being less willing and keen to help others the following day.”
The third part of the study involved mining a database of 3 million charitable donations in the United States between 2001 and 2016. Did the number of donations change after the transition to Daylight Saving Time and the potential loss of an hour of sleep? They found a 10% drop in donations. This same dent in compassionate gift-giving was not seen in regions of the country that did not change their clocks.
“Even a very modest ‘dose’ of sleep deprivation—here, just the loss of one single hour of sleep opportunity linked to daylight saving time—has a very measurable and very real impact on people’s generosity and, therefore, how we function as a connected society,” Walker said.
“When people lose one hour of sleep, there’s a clear hit on our innate human kindness and our motivation to help other people in need.”
An earlier study by Walker and Ben Simon showed that sleep deprivation forced people to socially withdraw and become more socially isolated. A lack of sleep also increased their feelings of loneliness. Worse still, when those sleep-deprived individuals interacted with other people, they spread their loneliness to those other individuals, almost like a virus, Walker said.
“Looking at the big picture, we’re starting to see that a lack of sleep results in a quite asocial and, from a helping perspective, anti-social individual, which has manifold consequences to how we live together as a social species,” he said.
“A lack of sleep makes people less empathetic, less generous, more socially withdrawn, and it’s infectious—there is contagion of loneliness.”
“The realization that the quantity and quality of sleep affects an entire society, caused by an impairment in prosocial behavior, may provide insights into our societal state of affairs in the present day,” Walker added.
This finding also offers a novel approach to improving these specific aspects of our society.
“Promoting sleep, rather than shaming people for sleeping enough, could very palpably help shape the social bonds we all experience every day,” Ben Simon said.
“Sleep, it turns out, is an incredible lubricant to prosocial, connected, empathic, kind and generous human behavior. In these divisive times, if there was ever a need for a strong, prosocial lubricant to enable the very best version of ourselves within society, now seems to be it,” said Walker, author of the international bestseller, Why We Sleep. “Sleep may be a wonderful ingredient that enables the alacrity of helping between human beings.”
“Sleep is essential for all aspects of our physical, mental and emotional lives,” Ben Simon said. “When sleep is undervalued in society, not only do we get sleep-deprived doctors, nurses and students, but we also suffer from unkind and less empathic interactions on a daily basis.”
In developed countries, more than half of all people report getting insufficient sleep during the work week.
“It is time as a society to abandon the idea that sleep is unnecessary or a waste and, without feeling embarrassed, start getting the sleep that we need,” she added. “It is the best form of kindness we can offer ourselves, as well as the people around us.”
About this sleep and psychology research news
Author: Press Office
Source: UC Berkeley
Contact: Press Office – UC Berkeley
Image: The image is credited to Eti Ben Simon and Matthew Walker, UC Berkeley
Original Research: Open access.
“Sleep loss leads to the withdrawal of human helping across individuals, groups, and large-scale societies” by Eti Ben Simon et al. PLOS Biology
Abstract
Sleep loss leads to the withdrawal of human helping across individuals, groups, and large-scale societies
Humans help each other. This fundamental feature of homo sapiens has been one of the most powerful forces sculpting the advent of modern civilizations. But what determines whether humans choose to help one another?
Across 3 replicating studies, here, we demonstrate that sleep loss represents one previously unrecognized factor dictating whether humans choose to help each other, observed at 3 different scales (within individuals, across individuals, and across societies).
First, at an individual level, 1 night of sleep loss triggers the withdrawal of help from one individual to another. Moreover, fMRI findings revealed that the withdrawal of human helping is associated with deactivation of key nodes within the social cognition brain network that facilitates prosociality.
Second, at a group level, ecological night-to-night reductions in sleep across several nights predict corresponding next-day reductions in the choice to help others during day-to-day interactions.
Third, at a large-scale national level, we demonstrate that 1 h of lost sleep opportunity, inflicted by the transition to Daylight Saving Time, reduces real-world altruistic helping through the act of donation giving, established through the analysis of over 3 million charitable donations.
Therefore, inadequate sleep represents a significant influential force determining whether humans choose to help one another, observable across micro- and macroscopic levels of civilized interaction.
The implications of this effect may be non-trivial when considering the essentiality of human helping in the maintenance of cooperative, civil society, combined with the reported decline in sufficient sleep in many first-world nations.






