New insights into ‘mental workspace’ may help advance artificial intelligence.
Philosophers and scientists have long puzzled over where human imagination comes from. In other words, what makes humans able to create art, invent tools, think scientifically and perform other incredibly diverse behaviors?
The answer, Dartmouth researchers conclude in a new study, lies in a widespread neural network, the brain’s “mental workspace” that consciously manipulates images, symbols, ideas and theories and gives humans the laser-like mental focus needed to solve complex problems and come up with new ideas.
Their findings, titled “Network structure and dynamics of the mental workspace,” appear the week of Sept. 16 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

“Our findings move us closer to understanding how the organization of our brains sets us apart from other species and provides such a rich internal playground for us to think freely and creatively,” says lead author Alex Schlegel, a graduate student in the Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences. “Understanding these differences will give us insight into where human creativity comes from and possibly allow us to recreate those same creative processes in machines.”
Scholars theorize that human imagination requires a widespread neural network in the brain, but evidence for such a “mental workspace” has been difficult to produce with techniques that mainly study brain activity in isolation. Dartmouth researchers addressed the issue by asking: How does the brain allow us to manipulate mental imagery? For instance, imagining a bumblebee with the head of a bull, a seemingly effortless task but one that requires the brain to construct a totally new image and make it appear in our mind’s eye.
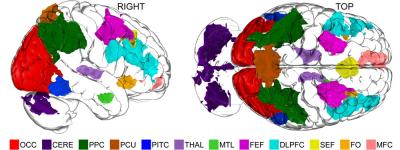
In the study, 15 participants were asked to imagine specific abstract visual shapes and then to mentally combine them into new more complex figures or to mentally dismantle them into their separate parts. Researchers measured the participants’ brain activity with functional MRI and found a cortical and subcortical network over a large part of the brain was responsible for their imagery manipulations. The network closely resembles the “mental workspace” that scholars have theorized might be responsible for much of human conscious experience and for the flexible cognitive abilities that humans have evolved.
Notes about this neuroscience research
This study was funded by a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship and by a Templeton Foundation Grant.
Contact: John Cramer – Dartmouth College
Source: Dartmouth College press release
Image Source: The image is credited to Alex Schlegel and is adapted from the Dartmouth College press release.
Original Research: Abstract for “Network structure and dynamics of the mental workspace” by Alexander Schlegel, Peter J. Kohler, Sergey V. Fogelson, Prescott Alexander, Dedeepya Konuthula, and Peter Ulric Tse in PNAS. Published online September 16 2013 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311149110