When tracking a moving object, the two halves of the human brain operate much like runners successfully passing a baton during a relay race, says a University of Oregon researcher.
In a study online ahead of print in Current Biology, electroencephalogram (EEG) measured brainwaves from healthy young adults revealed how information about an attended object — one being watched closely — moves from one brain hemisphere to the other.
Such handoffs are necessary because the human visual system is contralateral; objects on the left side of space are processed by the right hemisphere and vice versa. When objects change sides, the two hemispheres must coordinate so that the tracked object isn’t lost during the exchange.
“Attentional tracking is something we do on a regular basis when driving in traffic or walking through a crowd,” said Edward K. Vogel, professor of psychology. “Our world is dynamic. We’re moving. Our eyes are moving. Objects are moving. We need to use our attention to follow objects of interest as they move so that we can predict where they are going.”
People experience a smooth and seamless visual world despite information quickly being transferred back and forth between the hemispheres. “A car in your rearview mirror that moves from one lane to the other doesn’t suddenly disappear and then reappear on the other side,” he said. “The exchange is smooth, in part, because often the hemispheres coordinate a soft handoff.”
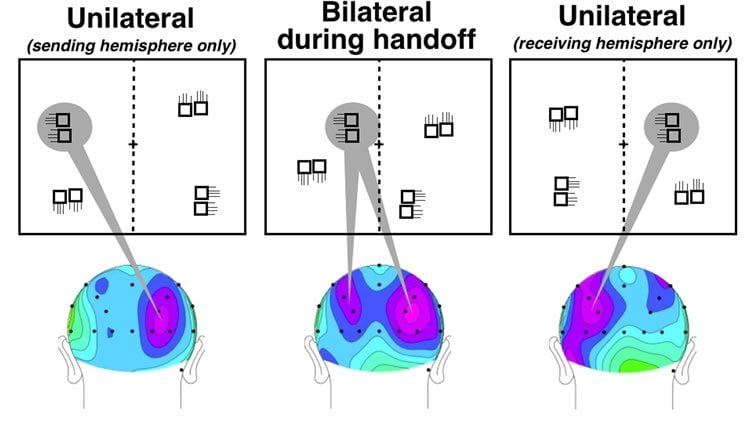
That means, he said, that before the object crosses into the other side of space, the new hemisphere picks it up, and the old hemisphere continues to hang on to it until it crosses well into the other side of space. Both hemispheres grab hold of the object during the exchange — much like in a relay race when two runners both briefly have hold of the baton to assure it isn’t dropped.
Eventually, Vogel said, such research may help us better understand individual differences in people’s visual tracking abilities. Some people, for instance, have trouble picking up a moving vehicle seen in a rearview mirror once it enters a blind spot. “This new technique allows us to watch the brain as information about a target is handed off from one side to the other, and it may provide insights into why attention is so limited,” Vogel said.
While psychological studies have often looked at attention and awareness, there has been little focus on how the two hemispheres interact. Interestingly, Vogel said, cellphone companies have long studied a similar problem: how to best transfer a call’s signal while a customer moves from one zone of a cell tower to another.
Cellular carriers using Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) such as Sprint and Verizon utilize a soft handoff between towers, similar to the new findings. Global System for Mobile (GSM) carriers, such as T-Mobile and ATT, use a hard handoff in which a signal leaving a tower’s coverage is rapidly shut off and then turned on by the next tower — a scenario that tended to, before the technology improved, result in more dropped calls.
“Researchers at the University of Oregon are using cutting-edge techniques to examine important mechanisms of cognitive functioning,” said Kimberly Andrews Espy, vice president for research and innovation and dean of the UO Graduate School. “This research by Dr. Vogel and his team provides a window on the process of attentional tracking that furthers our understanding of how the two hemispheres of the brain work together to process visual information.”
The National Institutes of Health (grants IF32EB011959, RO1MH077105 and R01MH65576), the Office of Naval Research (grants N00014-12-1-0972) and National Geospatial Agency (grant HM0177-13-1-0001_P00001) supported the research.
The paper’s lead author was former UO doctoral student Trafton Drew, who has since completed a postdoctoral fellowship at Harvard Medical School and about to join the University of Utah faculty. Additional co-authors with Vogel were UO graduate student Irida Mance and Harvard University faculty members Todd S. Horowitz and Jeremy M. Wolfe.
Contact: Jim Barlow – University of Oregon
Source: University of Oregon press release
Image Source: The image is credited to Trafton Drew and adapted from the University of Oregon press release
Original Research: Abstract for “A Soft Handoff of Attention between Cerebral Hemispheres” by Trafton Drew, Irida Mance, Todd S. Horowitz, Jeremy M. Wolfe, and Edward K. Vogel in Current Biology. Published online April 24 2014 doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.054