New findings from Carnegie Mellon identify altered ‘thought-markers’ of autism.
Psychiatric disorders, including autism, are characterized and diagnosed based on a clinical assessment of verbal and physical behavior. However, brain imaging and cognitive neuroscience are poised to provide a powerful advanced new tool.
Carnegie Mellon University researchers have created brain-reading techniques to use neural representations of social thoughts to predict autism diagnoses with 97 percent accuracy. This establishes the first biologically based diagnostic tool that measures a person’s thoughts to detect the disorder that affects many children and adults worldwide.
Published in PLoS One, the study combined functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and machine-learning techniques first developed at Carnegie Mellon that use brain activation patterns to scan and decode the contents of a person’s thoughts of objects or emotions. The previous work also demonstrated that specific thoughts and emotions have a very similar neural signature across normal individuals, suggesting that brain disorders may display detectable alterations in thought activation patterns.
Now, the research team led by CMU’s Marcel Just has successfully used this approach to identify autism by detecting changes in the way certain concepts are represented in the brains of autistic individuals. They call these alterations “thought-markers” because they indicate abnormalities in the brain representations of certain thoughts that are diagnostic of the disorder.
“We found that we could tell whether a person has autism or not by the their brain activation patterns when they think about social concepts. This gives us a whole new perspective to understanding psychiatric illnesses and disorders,” said Just, the D. O. Hebb University Professor of Psychology in the Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences and a leading researcher into the neural basis of autism. “We’ve shown not just that the brains of people with autism may be different, or that their activation is different, but that the way social thoughts are formed is different. We have discovered a biological thought-marker for autism.”
For the study, Just and his colleagues scanned the brains of 17 adults with high-functioning autism and 17 neurotypical control participants. The participants were asked to think about 16 different social interactions, such as “persuade,” “adore” and “hug.”
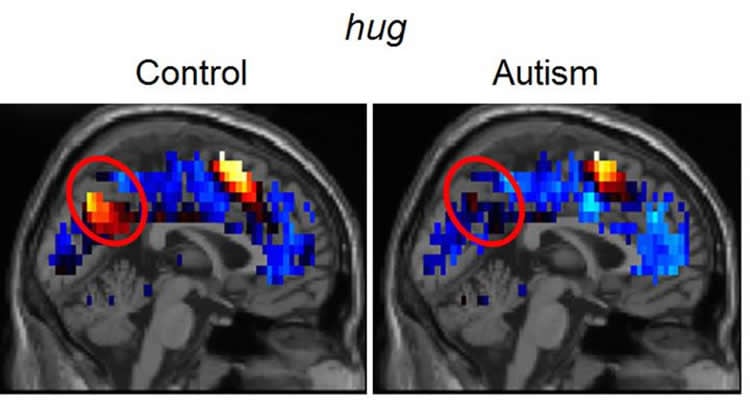
The resulting brain images showed that the control participants’ thoughts of social interaction clearly included activation indicating a representation of the “self,” manifested in the brain’s posterior midline regions. However, the self-related activation was near absent in the autism group. Machine-learning algorithms classified individuals as autistic or non-autistic with 97 percent accuracy based on the fMRI thought-markers.
“When asked to think about persuading, hugging or adoring, the neurotypical participants put themselves into the thoughts; they were part of the interaction. For those with autism, the thought was more like considering a dictionary definition or watching a play – without self-involvement,” Just said.
Implications of this research could extend to other psychiatric disorders, such as being suicidal or having obsessive-compulsive disorder, in which certain types of thoughts are altered. By providing a brain-based measure of the altered thoughts to use in conjunction with clinical assessments, this new research could enable clinicians to make quicker and more certain diagnoses and more quickly implement targeted therapies that focus on the alteration.
Carnegie Mellon Researchers Accurately Predict Autism Diagnosis Based on Brain Representations
“This is a potentially extremely valuable method that could not only complement current psychiatric assessment. It could identify psychiatric disorders not just by their symptoms but by the brain systems that are not functioning properly. It may eventually be possible to screen for psychiatric disorders using quantitative biological measures of thought that would test for a range of illnesses or disorders,” Just said.
This neuroscience research is on the vanguard of two fronts: it advances the scientific mission of classifying and diagnosing mental disorders based on behavioral and neurobiological measures (rather than conventional symptoms), and it integrates the conception of brain and mind by assessing thoughts in terms of brain function.
In addition to Just, the research team included CMU’s Vladimir L. Cherkassky, Augusto Buchweitz, Timothy A. Keller and Tom M. Mitchell.
The National Institute of Mental Health funded this research.
Contact: Shilo Rea – Carnegie Mellon University
Source: Carnegie Mellon University press release
Image Source: The image is credited to Carnegie Mellon University and is adapted from the press release
Video Source: The video is available at the CMUHSS YouTube page
Original Research: Full open access research for “Identifying Autism from Neural Representations of Social Interactions: Neurocognitive Markers of Autism” by Marcel Adam Just, Vladimir L. Cherkassky, Augusto Buchweitz, Timothy A. Keller, and Tom M. Mitchell in PLOS ONE. Published online December 2 2014 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113879
Identifying Autism from Neural Representations of Social Interactions: Neurocognitive Markers of Autism
Autism is a psychiatric/neurological condition in which alterations in social interaction (among other symptoms) are diagnosed by behavioral psychiatric methods. The main goal of this study was to determine how the neural representations and meanings of social concepts (such as to insult) are altered in autism. A second goal was to determine whether these alterations can serve as neurocognitive markers of autism. The approach is based on previous advances in fMRI analysis methods that permit (a) the identification of a concept, such as the thought of a physical object, from its fMRI pattern, and (b) the ability to assess the semantic content of a concept from its fMRI pattern. These factor analysis and machine learning methods were applied to the fMRI activation patterns of 17 adults with high-functioning autism and matched controls, scanned while thinking about 16 social interactions. One prominent neural representation factor that emerged (manifested mainly in posterior midline regions) was related to self-representation, but this factor was present only for the control participants, and was near-absent in the autism group. Moreover, machine learning algorithms classified individuals as autistic or control with 97% accuracy from their fMRI neurocognitive markers. The findings suggest that psychiatric alterations of thought can begin to be biologically understood by assessing the form and content of the altered thought’s underlying brain activation patterns.
“Identifying Autism from Neural Representations of Social Interactions: Neurocognitive Markers of Autism” by Marcel Adam Just, Vladimir L. Cherkassky, Augusto Buchweitz, Timothy A. Keller, and Tom M. Mitchell in PLOS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113879.







