People with mild cognitive impairment are at higher risk of developing dementia if they have diabetes or psychiatric symptoms such as depression, finds a new review led by UCL researchers.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a state between normal ageing and dementia, where someone’s mind is functioning less well than would be expected for their age. It affects 19% of people aged 65 and over, and around 46% of people with MCI develop dementia within 3 years compared with 3% of the general population.
The latest review paper, published in the American Journal of Psychiatry, analysed data from 62 separate studies, following a total of 15,950 people diagnosed with MCI. The study found that among people with MCI, those with diabetes were 65% more likely to progress to dementia and those with psychiatric symptoms were more than twice as likely to develop the condition.
“There are strong links between mental and physical health, so keeping your body healthy can also help to keep your brain working properly,” explains lead author Dr Claudia Cooper (UCL Psychiatry). “Lifestyle changes to improve diet and mood might help people with MCI to avoid dementia, and bring many other health benefits. This doesn’t necessarily mean that addressing diabetes, psychiatric symptoms and diet will reduce an individual’s risk, but our review provides the best evidence to date about what might help.”
The Alzheimer’s Society charity recommends that people stay socially and physically active to help prevent dementia. Their guidelines also suggest eating a diet high in fruit and vegetables and low in meat and saturated fats, such as the Mediterranean diet.
“Some damage is already done in those with MCI but these results give a good idea about what it makes sense to target to reduce the chance of dementia,” says senior author Professor Gill Livingston (UCL Psychiatry). “Randomised controlled trials are now needed.”
Professor Alan Thompson, Dean of the UCL Faculty of Brain Sciences, says: “This impressive Systematic Review and meta-analysis from The Faculty of Brain Science’s Division of Psychiatry underlines two important messages. Firstly, the impact of medical and psychiatric co-morbidities in individuals with mild cognitive impairment and secondly, the importance and therapeutic potential of early intervention in the prevention of dementia. Confirming these findings and incorporating appropriate preventative strategies could play an important part in lessening the ever-increasing societal burden of dementia in our ageing population.”
Contact: Harry Dayantis – UCL
Source: UCL press release
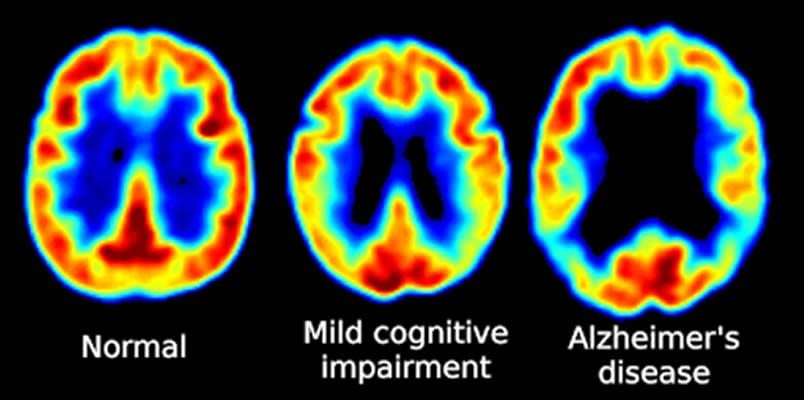
Image Source: The image is credited to Center For Functional Imaging, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and is in the public domain.
Original Research: Abstract for “Modifiable Predictors of Dementia in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis” by Claudia Cooper, Ph.D., M.R.C.Psych.; Andrew Sommerlad, M.R.C.Psych.; Constantine G. Lyketsos, M.D., M.H.S.; and Gill Livingston, M.D., F.R.C.Psych. in American Journal of Psychiatry. Published online February 18 2015 doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14070878